UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE






Are Beans Good For Diabetics, Should they have them?


Table of Contents
- Should people With Diabetes have Beans?
- Are there Health Benefits to Eating More beans?
- Fiber Content
- Vitamins and Minerals
- Antioxidants
- What Types Of Beans Should Diabetics Have?
- Black Beans
- White Beans
- Lentils
- Kidney Beans
- Green Beans
- SugarMD DiaVitamin and Neuropathy Support
- How Much Should People With Diabetes Eat?
- Potential Risks of Eating Beans With Diabetes
- Conclusion
- About The Author
Eating beans can be an essential part of a healthy diet, but are beans good for diabetics? Not only can they provide a variety of essential vitamins and minerals, but they are also high in dietary fiber and antioxidants, making them beneficial for overall health.
In this article, we discuss the potential health benefits and risks of including beans in a diabetes-friendly diet. We will also provide information on the types and amounts of beans that people with diabetes should have. Read on to learn more about beans and diabetes!
Should people With Diabetes have Beans?
Beans are a type of legume that can be a great option for those with diabetes. They are packed with nutrition and are great sources of dietary fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals. Eating beans can help regulate blood sugar levels and can also reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Beans are also a low-GI food, meaning they release their sugar more slowly than other carbohydrate sources, making them a good option for those with diabetes.
Studies have shown that consuming beans on a regular basis is beneficial for those with diabetes. Cooked dried legumes have been shown to stimulate low blood glucose responses, and their consumption by individuals with diabetes has been encouraged. Eating beans has been linked to improved blood sugar and cholesterol levels in those with diabetes, as well as improved glycemic control. Beans can be a great source of nutrients for people with diabetes.
They are low in fat, high in dietary fiber, and contain several key vitamins and minerals. Beans are also a great source of plant proteins, making them an ideal choice for those who are vegetarian or vegan. Including beans in a diabetes-friendly diet can offer a number of health benefits. Beans are full of nutrition and fiber, making them a beneficial choice for those with diabetes.
They are also low in fat, contain essential vitamins and minerals, and can help regulate blood sugar levels. Eating beans regularly can be a great way to help improve overall health for those with diabetes.
Are there Health Benefits to Eating More beans?
Beans are high in fiber and a great source of plant-based protein, which makes them a nutritious choice for people with diabetes. Eating beans can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels, as they're low in glycemic index.
In addition, beans are packed with vitamins like folate, magnesium, zinc, and iron. Furthermore, they're high in dietary fiber which helps promote regularity, improve digestion, and aid weight management. In fact, adding beans to a diabetic meal plan can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In addition, beans may help lower cholesterol levels, as they contain soluble fiber, which binds to and removes cholesterol from the body. Eating beans can also help regulate digestion and reduce the risk of developing constipation.
Fiber Content
Eating a diet high in fiber helps with blood sugar control. Studies have shown that people with diabetes who eat a diet rich in beans have lower blood glucose levels, compared to those who do not eat beans.
Additionally, fiber-rich foods can help slow down the absorption of sugar and carbohydrates, thus reducing short-term spikes in blood sugar levels. The American Diabetes Association recommends that people with diabetes consume 20-35 grams of fiber per day. One cup of cooked beans provides anywhere from 9-13 grams of fiber.
Beans are also low in calories and do not contain any saturated fat, which makes them an ideal addition to any diabetes-friendly diet. While beans are good for people with diabetes, it is important to be aware that some beans - such as chickpeas, lentils, and black beans - are higher in carbohydrates.
As such, it is a good idea to monitor carbohydrate intake when including beans in one’s diet. Eating a balanced meal containing protein, fat, and carbohydrates can help prevent sharp spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, combining beans with other foods like vegetables, grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar.
Vitamins and Minerals
Beans contain numerous essential vitamins and minerals that can be beneficial for individuals with diabetes. They contain small amounts of vitamins A, B6, B12, C, E, and K as well as folate, choline, thiamin, and riboflavin. Beans are also a good source of minerals including calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc.
Beans also contain powerful antioxidants that can help protect against long-term complications of diabetes such as kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision loss. These antioxidants include flavonoids, lignans, anthocyanins, and coumarins, all of which have been shown to have a positive effect on blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, beans can be a great choice for people with diabetes because of their high nutrient content, high fiber content, and powerful antioxidants. They can help to manage blood sugar levels and protect against the long-term complications of diabetes.
Antioxidants
Studies have shown that the antioxidants found in beans can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which can be problems for those with diabetes. Additionally, beans are low in glycemic index, which makes them a great choice for diabetics. Overall, beans can be a great addition to a diabetic-friendly diet.
They are low in glycemic index and rich in components such as antioxidants, dietary fiber, and protein, which can help people with diabetes manage their condition. Therefore, beans can be a great option for people with diabetes.
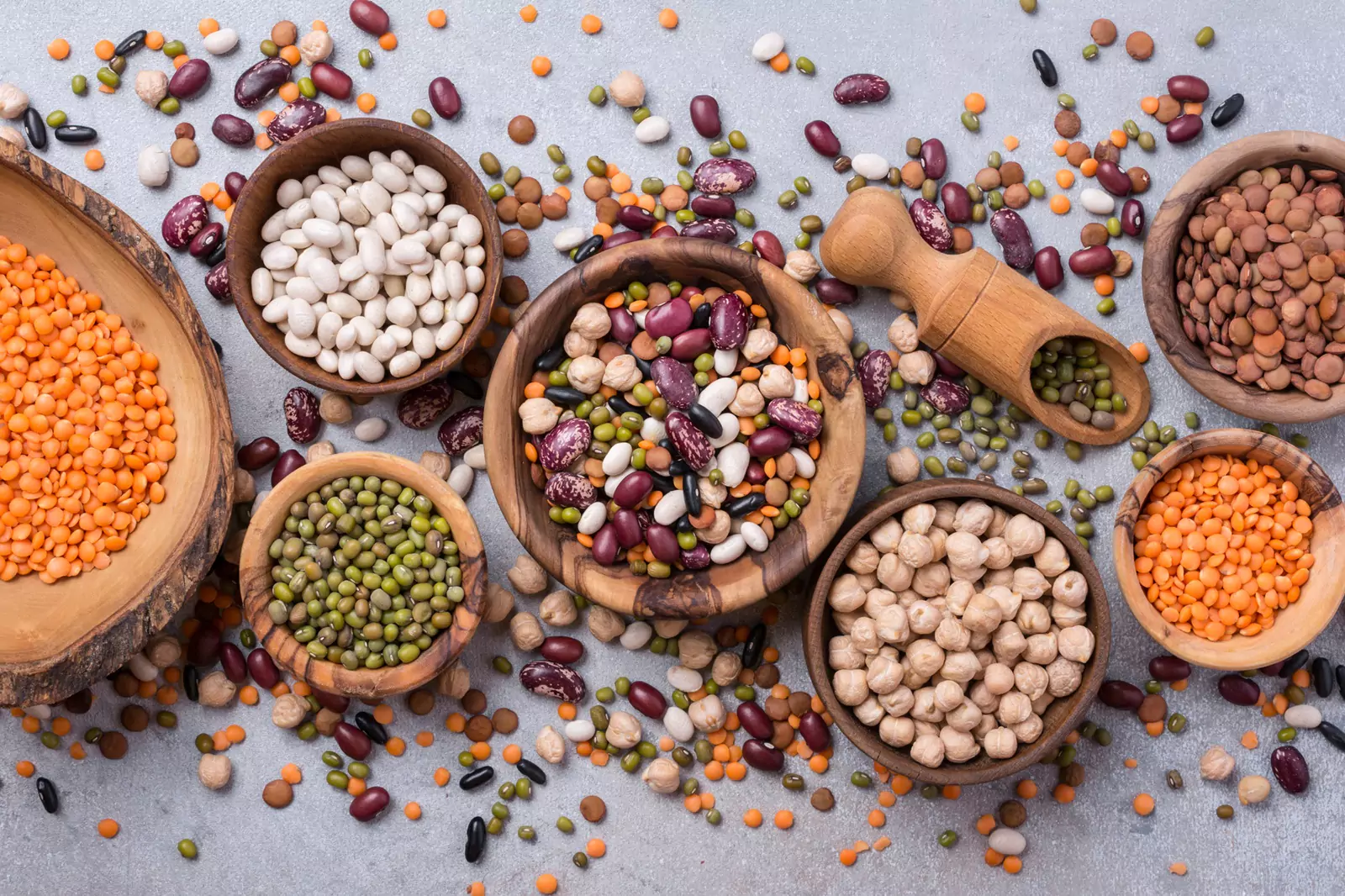
What Types Of Beans Should Diabetics Have?
Dark, red, and black beans are usually the most beneficial for people with diabetes due to their low glycemic index. These common beans are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help support health and keep blood sugar levels in check.
Lentils are also a great choice, as they have a lower glycemic index and a higher content of dietary fiber. Eating a variety of different types of beans, choosing low-sugar options, and eating in moderation can ensure that diabetics are able to enjoy the health benefits of beans while managing their diabetes.
Black Beans
Black beans are a type of legume, a plant-based protein source that has been consumed in many parts of the world for centuries. While the exact nutritional content of black beans varies depending on preparation and serving size, they are generally a good source of fiber, folate, copper, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, and zinc.
Black beans are also a source of protein and carbohydrates. The fiber and protein content of black beans may help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, which can reduce the spike in blood sugar levels that often follow a meal.
Additionally, black beans have a low glycemic index and can help keep glucose levels stable for those with diabetes. While the exact nutritional content of black beans varies depending on preparation and serving size, research has suggested that incorporating black beans into a diabetes-friendly diet can be beneficial. Replacing refined grains with black beans can help increase the amount of fiber in the diet and regulate blood sugar levels.
Beans are a great alternative to meat and other animal products and are also a good source of vegetarian and vegan protein. When choosing black beans, be sure to select those that are canned or dried, as canned beans may contain added salt, sugar, and other additives. Also, look for low-sodium varieties if possible.
To get the most nutrients from black beans, rinse canned beans before using and soak dry beans for at least six hours before cooking. In summary, evidence suggests that people with diabetes may benefit from consuming black beans, as they are a low glycemic index food and have properties that can help keep glucose levels stable.
Black beans are a healthy, plant-based alternative to animal products and can help increase fiber intake, which can be beneficial for those with diabetes. When selecting beans, be sure to check labels for added ingredients and rinse canned beans before using. Soaking dry beans for at least six hours before cooking can also help maximize the nutritional benefits of black beans.
White Beans
When it comes to the glycemic index, white beans have a moderate ranking. This means that, when eaten in moderation, they will not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Therefore, white beans can be safely consumed by people with diabetes without worrying about dangerously high blood sugar levels.
However, it is important to be mindful of portion sizes when eating white beans as they are higher in carbohydrates than some other types of beans. For people with diabetes, it is best to consume a moderate portion size of white beans in combination with other healthy, low-glycemic side dishes.
In addition to the health benefits that white beans can offer, they are also quite versatile and can be added to a variety of different recipes. They are great in soups, salads, and casseroles, and can also be used as a topping for bruschetta.
Lentils
Lentils are a popular choice among people with diabetes. Many varieties of legumes, including lentils, are high in fiber and contain complex carbohydrates that can help stabilize blood sugar levels. This makes them a great meal option for those with diabetes. Furthermore, lentils are extremely versatile and can be used in soups, stews, salads, and other dishes.
Studies have shown that people with diabetes who eat a diet that includes legumes have better glycemic control. Eating legumes can also help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. They are low in saturated fats and contain a variety of essential nutrients including iron, magnesium, and protein.
Additionally, lentils are a good source of antioxidants which can help reduce inflammation in the body and protect against diabetes-related complications. Eating lentils can also help reduce cholesterol levels and may even help with weight management.
Kidney Beans
When considering if people with diabetes should have beans, it's important to look at the type of beans being included in the diet. Kidney beans, in particular, are often considered a good choice for diabetes management. On one hand, they are a good source of carbohydrates, so they provide much-needed energy to diabetics who may have low blood sugar levels or feel fatigued.
On the other hand, they also contain lots of dietary fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing diabetes-related complications such as heart disease and stroke. In addition, kidney beans are also a good source of protein, which is essential for a healthy diet.
Dietary fiber helps to slow the absorption of sugar, giving diabetics more time to manage their blood sugar levels. This is especially important for type 2 diabetics, who are vulnerable to large blood sugar spikes if their diets contain too many simple carbohydrates.
Kidney beans also have a low glycemic index, which means that they don’t cause rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar levels. All in all, kidney beans are an excellent choice for diabetics, as they provide beneficial energy as well as dietary fiber and protein.
They can be eaten in a variety of ways, such as in soups, stews, and salads, providing a delicious and nutritious component to a meal. As they are relatively low in calories and fat, they are suitable for people who are trying to manage their weight. However, it is important to remember that portion size is key; the recommended portion size for kidney beans is 1/2 cup of cooked beans.
Green Beans
For those with diabetes, green beans are an excellent choice as a good source of dietary fiber and contain many vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They can be eaten cooked or raw, and they can also be used in salads and soups. They are a great addition to any healthy diet. Beans are a good source of complex carbohydrates.
Complex carbohydrates are healthier for diabetics than refined carbohydrates, as they are broken down more slowly, causing a reduced impact on blood sugar levels. Green beans contain more complex carbohydrates than other beans, such as kidney beans, so they are a great option for diabetics. In terms of vitamins and minerals, green beans are a great source of vitamin A, calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Vitamin A is important for vision, calcium helps to build strong bones, magnesium helps to regulate blood sugar levels, and potassium helps to lower blood pressure. All these vitamins and minerals are known to help with diabetes management. Green beans also contain antioxidants, which help to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
Oxidative stress and inflammation can both contribute to the development of diabetes, so it is important to reduce these factors. Antioxidants can also reduce the risk of disease and help with the healing process.
SugarMD DiaVitamin and Neuropathy Support
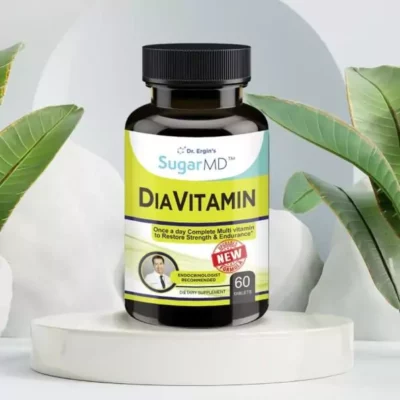

SugarMD DiaVitamin and SugarMD Neuropathy Support 180 Capsules are dietary supplements designed to support the health of individuals with diabetes. The DiaVitamin formula is formulated to support healthy glucose metabolism and provides essential vitamins and minerals including High potency B-vitamins, Antioxidant Vitamins A, C, E, Thiamine, and Selenium, while the Neuropathy Support formula is designed to help alleviate nerve pain and support nerve health.
Both formulas are made with high-quality ingredients and are carefully crafted to meet the unique needs of individuals with diabetes. Support into your daily regimen, you can help support overall health and wellness, especially for those with diabetes.
How Much Should People With Diabetes Eat?
When deciding how much beans to include in your diet, it is important to consider the type of beans you are eating and how they interact with your diabetes. For example, red kidney beans are known to be lower in carbohydrates than a white cup of beans, making it an ideal choice for people with diabetes. However, it is important to remember that beans are still high in carbohydrates and can have an effect on your blood sugar if consumed in large quantities.
It is recommended that people with diabetes include a moderate amount of beans in their diets, in order to gain the most benefit without putting too much strain on their blood sugar levels. If you are unsure whether a certain type of bean is recommended for diabetics, consult your doctor or dietitian for advice.
In general, it is a good idea to try and include a variety of beans in your meals, such as black beans, chickpeas, navy beans, red kidney beans, and pinto beans. Including a variety of beans will ensure you get the most benefit out of their nutrients and that you don’t miss out on any essential vitamins and minerals.
Potential Risks of Eating Beans With Diabetes
While beans are generally considered to be a healthy addition to a diet for anyone, those with diabetes must consider a few potential risks before deciding if beans are a good fit for their diet. One of the main concerns with beans and diabetes is their carbohydrate content. Beans are a source of carbohydrates, and people with diabetes must carefully monitor their carbohydrate consumption to ensure their blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range.
Additionally, the type of carbohydrate found in some beans is a form of starch. This type of carbohydrate is more slowly converted into sugar, meaning it takes longer for the blood sugar effects to be seen. However, this slow digestion process can make it more difficult to track and could lead to spikes in blood sugar which can be harmful to those with diabetes.
Finally, those with diabetes should be aware of the potential to overeat when consuming beans. Because they are high in dietary fiber, they can fill the stomach quickly and can easily lead to overeating if not monitored carefully. Overeating can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which can be harmful for those with diabetes.
In conclusion, for people with diabetes, the decision to include beans in their diet should be made carefully with the help of a medical professional. While beans are generally considered to be a healthy addition to the diet, those with diabetes must consider the potential risks before deciding whether or not beans are a good fit for their diet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, beans are an excellent addition to any diet, especially for those with diabetes. They are a great source of fiber, vitamins and minerals, antioxidants, and other healthful nutrients. Black beans, white beans, lentils, kidney beans, and green beans all make excellent choices for people with diabetes.
The recommended amount and type of beans will depend on the individual and their particular health needs, but in general, people with diabetes should aim to include beans as a part of their daily diet. While some potential risks should be considered, it is important to remember that the health benefits of beans far outweigh the risks.
Eating beans may help improve blood sugar control, reduce inflammation, and promote healthy weight management, making them a great addition to the diabetes diet.
About The Author
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of "The Ultimate Diabetes Book," and founder of "the SugarMD YouTube channel." Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively.
Disclaimer: The website's disease and treatment info is general guidance and not a substitute for professional healthcare advice. Seek professional advice for personalized diagnosis and treatment plans to ensure accurate and effective care. Consult a qualified healthcare professional for any questions about your health and wellness.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
466 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products