UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE
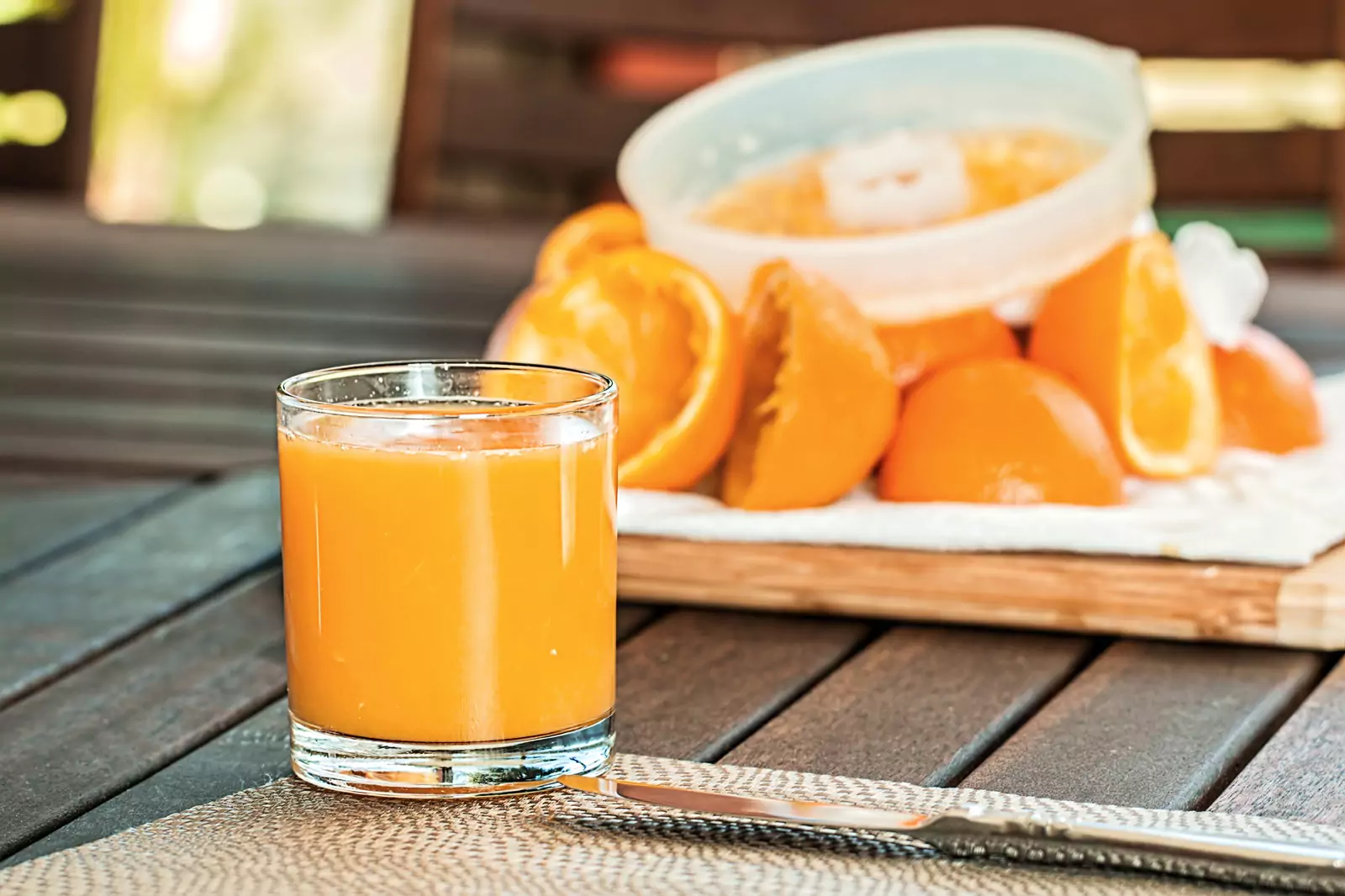






Is Orange Juice Good For Diabetics?


Table of Contents
- What Are The Benefits To Having Orange Juice While Diabetic?
- Orange Juice Is A Great Source Of Vitamin C
- Orange Juice Is A Great Source Of Potassium
- Orange Juice Provides Folate
- Downsides To Having Orange Juice While Diabetic
- Nothing Wrong With It
- Should You Drink Orange Juice If You Have Type Two Diabetes?
- Yes, It Can Be A Part Of The Diet
- Orange Juice Gives Vitamin C, Folate and Fibre
- Does Orange Juice Raise your Blood Sugar levels?
- Recommendations for Diabetics
- Conclusion
- About The Author
For diabetics, it is often wise to be mindful of what goes into their diet. One of the most popular drinks out there that is often consumed is orange juice, but is it actually a safe option for diabetics? In this article we will explore if orange juice is a good choice for diabetics, looking at the nutritional benefits, how it affects blood sugar and what our recommendations are.
What Are The Benefits To Having Orange Juice While Diabetic?
Orange juice is loaded with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help promote better health and wellness. One of the key nutrients found in orange juice is Vitamin C, which is known for its immune boosting properties. Orange juice also provides essential minerals, including calcium, which is essential for bone health and helps to regulate blood sugar levels.
Potassium, magnesium, and zinc are all found in orange juice, and these minerals play a role in blood sugar control. Finally, orange juice is a good source of dietary fiber, which is important for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome and can promote better digestion. Let’s talk about these benefits in detail.
Orange Juice Is A Great Source Of Vitamin C
Orange juice is a great source of Vitamin C and other essential nutrients, which makes it a good choice for diabetics. While drinking orange juice can provide many health benefits, diabetics should be aware of the sugar content of orange juice and be sure to carefully monitor their blood sugar levels when consuming orange juice.
The American Diabetes Association guidelines suggest that diabetics should limit their intake of sugar-sweetened beverages, including orange juice. Orange juice has a high sugar content, so it is important to consume it in moderation in order to prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Diabetics should also look for low-sugar varieties of orange juice, such as brands made with no added sugar or sweeteners.
Orange Juice Is A Great Source Of Potassium
Orange juice is an ideal food item to include in the diet of a diabetic, as it is rich in essential nutrients and can help keep diabetes under control. One of these nutrients is potassium. Potassium is an important mineral and plays a role in regulating the body’s fluid balance. It helps to control blood pressure and heart rate and has been known to help reduce the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular problems.
Orange juice is an excellent source of potassium and can provide around 250-300 milligrams of this mineral in just a single cup. It is also high in Vitamin C, which helps to support the immune system and can help prevent colds and other infections, which are common in people with diabetes.
Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a role in maintaining healthy blood pressure, heart function, and fluid balance in the body. It's recommended to consume at least 4.7 grams of potassium per day. Orange juice is a good source of potassium and it's a tasty way to increase your intake of this important mineral.
Orange Juice Provides Folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9, is an essential nutrient that is important for many bodily functions, including the formation of red blood cells, the proper function of the nervous system, and the synthesis of DNA. Folate is particularly important for diabetics as it has been shown to help lower the risk of certain diabetes-related complications.
Orange juice is a good source of folate. This can be beneficial for diabetics as adequate intake of folate has been shown to help lower the risk of certain diabetes-related complications such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy. Folate works together with vitamin B12 and vitamin B6 to control the levels of homocysteine in the blood. High homocysteine levels have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in diabetics.
Adequate intake of folate can help to lower homocysteine levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, folate is important for the formation of red blood cells and the proper function of the nervous system, which can be affected in diabetics with neuropathy.
However, it's important to keep in mind that folate is just one of many important nutrients for people with diabetes. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is recommended for optimal health for everyone, including diabetics.
Downsides To Having Orange Juice While Diabetic
When it comes to managing diabetes and overall health, orange juice should not be overlooked. Orange juice is a great addition to the daily diet for diabetics — it is nutrient-dense and contains powerful antioxidants that can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation and support optimal health.
Nothing Wrong With It
When it comes to diabetics, the question of whether orange juice is safe and healthy to consume is often brought up. The good news is that there is absolutely nothing wrong with orange juice and it can absolutely be consumed by those with diabetes. Orange juice can be part of a healthy and balanced diet, and can even be beneficial to those managing their diabetes.
Orange juice is a nutrient-rich beverage that is low in calories and has a high level of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Orange juice can also be a great substitute for unhealthy snacks, like candy and processed snacks. That being said, it is important to keep in mind that orange juice should still be consumed in moderation and not become the primary source of hydration when managing diabetes.
It is also important to pay attention to the serving size since the calorie and sugar content can add up quickly if you’re not monitoring your intake. Overall, orange juice is a safe and healthy beverage for diabetics. It provides a variety of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants and has a low glycemic index. As long as it is consumed in moderation and in recommended servings, diabetics should not have any issues with consuming orange juice as part of a balanced and healthy diet.
Should You Drink Orange Juice If You Have Type Two Diabetes?
The answer to the question of whether or not orange juice is safe for diabetics to consume is a resounding yes, with a few caveats. Orange juice is actually a great choice for diabetics, as it contains lots of vitamins and minerals.
Yes, It Can Be A Part Of The Diet
It is possible for diabetics to enjoy a moderate amount of orange juice, as it does provide some health benefits. Orange juice is a good source of vitamin C, folate, and potassium - all of which are important for people with diabetes. While orange juice naturally contains sugar, it can be part of a balanced diet for those with diabetes if it is consumed in moderation.
The key for diabetic patients when consuming orange juice is to make sure you are aware of the sugar and carbohydrate content of the beverage. Though it contains naturally occurring sugar, many brands of orange juice also contain added sugar, which can raise blood sugar levels quickly.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends that people with diabetes limit their intake of added sugars and that diabetics should look for brands of orange juice that are 100% pure with no added sugar.
ADA does recommend that people with diabetes should strive to limit their daily intake of carbohydrates to 45-60 grams per meal and 15-20 grams per snack. This is because carbohydrates are broken down into glucose (sugar) in the body, which can affect blood sugar levels.
However, it's important to note that the specific carbohydrate intake recommendations may vary based on individual needs and diabetes management plans, and it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. In conclusion, orange juice can be a part of a diabetic’s diet, but it should be consumed in moderation and with caution.
Knowing the sugar, carbohydrate, and nutrient content of the juice is key, and diabetics should always monitor their blood sugar levels after consuming it. When consumed mindfully, orange juice can be a healthy, refreshing part of a diabetic’s balanced diet.
Orange Juice Gives Vitamin C, Folate and Fibre
One of the key benefits of orange juice for people with diabetes type 2 is its high vitamin C content. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays a role in maintaining the health of the immune system, skin, and blood vessels. It's also a powerful antioxidant that can help protect against free radicals that can cause damage to cells in the body. Another important nutrient found in orange juice is folate, also known as vitamin B9.
Folate is an essential nutrient that is important for many bodily functions, including the formation of red blood cells, the proper function of the nervous system, and the synthesis of DNA. Adequate intake of folate can help to lower homocysteine levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is a common complication of diabetes type 2.
In addition, Orange juice contains some fiber, that can help with digestion, and may help to lower blood sugar levels. Fiber slows down the absorption of carbohydrates, which can help to keep blood sugar levels stable. Fiber also promotes regular bowel movements and can help to lower cholesterol levels. It's important to note that orange juice is not a low-carbohydrate drink, so it's important to consume it in moderation.
A serving size of orange juice is typically 4 ounces, or half a cup, which contains around 10 grams of carbohydrates. For diabetics, it's important to adjust their meal and snack portions appropriately to fit the juice into their daily carbohydrate intake. It's also important to look for brands of orange juice that are 100% pure with no added sugar.
In conclusion, Orange juice can be a nutritious addition to a diabetes type 2 diet when consumed in moderation. It provides vitamin C, folate, and fiber which are essential for a healthy diet. However, it's important for diabetics to pay attention to their intake of carbohydrates and added sugars. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is always recommended.
Does Orange Juice Raise your Blood Sugar levels?
The answer to the question “Is orange juice safe for diabetics?” is a complicated one. While there are many benefits that come with drinking orange juice, it is important to consider that it may have some negative effects on blood sugar and insulin levels. Orange juice contains high levels of natural sugars and carbohydrates, making it a source of fuel for the body and a source of glucose when your blood sugar levels are low.
In the short term, orange juice may help to boost your energy and provide a quick boost of glucose to the body in the form of simple sugars. However, in the long term, this can lead to a major spike in your blood sugar levels, resulting in the need for additional insulin. Some diabetics report that they can drink orange juice without an issue, as long as they take their insulin soon afterward.
Others will opt for a more sugar-free version, such as sugar-free orange juice. While this version does not provide the same quick-fix of glucose as regular orange juice, it does reduce the amount of sugar entering the bloodstream, which can help prevent large spikes in blood sugar levels.
To make sure that you are making the best decisions for your health, it is important to talk to your doctor. They will be able to advise you on the best course of action when it comes to consuming orange juice and managing your diabetes.
Recommendations for Diabetics
First, it is important to understand that orange juice contains natural sugars and can raise blood sugar levels. Sugars can also raise triglycerides, which are a lipoproteins found in the blood. Elevated triglycerides can also increase a person's risk for cardiovascular disease.
To ensure that your blood sugar levels remain stable, it is important to consume orange juice in moderation. Orange juice should be considered a treat, and not a staple of your diet. Drinking orange juice once a day is usually considered safe, but try not to drink more than that. Another factor to consider is that orange juice has a relatively high glycemic index, which means that it can cause a spike in blood sugar levels.
In addition, it is important to choose juices that are made from only natural, whole oranges or that are free of added sugar. Finally, it is important to be mindful of the other ingredients in orange juice. Many orange juices have been sweetened or flavored with preservatives, artificial colors, and other additives. These ingredients can all have an adverse effect on blood sugar levels, so it is important to check labels carefully and avoid any juices that contain these ingredients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, orange juice can be an excellent drink for diabetics. It is packed with many beneficial vitamins and minerals and can be an important part of a healthy diet. Orange juice will not raise blood sugar levels, nor will it cause adverse reactions in diabetics. As such, diabetics should feel free to include orange juice in their daily diet, as long as it is drunk in moderation.
A sensible and balanced diet should always take priority over consuming solely orange juice when managing diabetes. Ultimately, orange juice can be a great addition to any health and well-being plan, and it can give diabetics an extra nutrient boost to help them reach their goals.
About The Author
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin's journey in the medical field began with earning his medical degree with honors from Marmara University School of Medicine in Istanbul, Turkey. He then went on to complete his internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic, one of the top medical centers in the United States, located in Cleveland, Ohio.
With a wealth of knowledge and experience in his field, Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, making him a respected and highly qualified physician. He is also a certified diabetes education specialist, author of the book "The Ultimate Diabetes Book" and the founder of the SugarMD YouTube channel, where he shares valuable insights and information on diabetes management and care. Currently, Dr. Ergin practices in Port Saint Lucie, FL, where he provides exceptional care to his patients and helps them to effectively manage their diabetes.
It is important to note that the information on diseases and treatments provided on this website is for general guidance only and should never be considered a substitute for the advice provided by a qualified healthcare professional. Always seek the advice of your physician, health provider, or other qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding your health.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
466 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products