UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE






Debunking the Misconceptions of A1c Levels


Table of Contents
- Understanding A1c Levels
- Misconception 1: A1c Levels are the Only Indicator of Diabetes Control
- Misconception 2: A 'Normal' A1c Level Means No Diabetes
- Misconception 3: Lower A1c Levels are Always Better
- Misconception 4: A1c Levels Can Be Lowered Quickly
- Misconception 5: A1c Test Results are Always Accurate
- Misconception 6: A1c Levels are the Same for Everyone
- Misconception 7: A1c Levels Can Determine Daily Blood Sugar Levels
- Misconception 8: A High A1c Level Means Immediate Complications
- Misconception 9: A1c Levels Can Be Managed Without Lifestyle Changes
- Misconception 10: A1c Levels are Only Important for People with Diabetes
- The Truth About Managing A1c Levels
- The Role of Medical Professionals in Managing A1c Levels
- About The Author
In the fascinating world of health and wellness, one area that continues to be surrounded by ambiguity and misconceptions is the A1c level – a significant benchmark in diabetes management. It's astonishing, considering the critical role that A1c levels play, how it can often be misunderstood.
This article aims to break down these misconceptions and provide a clear, comprehensive understanding of A1c levels. A1c levels bear considerable weight in the management of diabetes. Why so, you ask? A patient's A1c level is a telling indicator of the average blood sugar level over the past few months.
It's a crucial piece in the puzzle of diabetes management. However, a handful of misconceptions associated with these levels can hinder an individual's efforts to manage their condition effectively. This article addresses these misconceptions head-on and clarifies the true nature of A1c levels.
Understanding A1c Levels
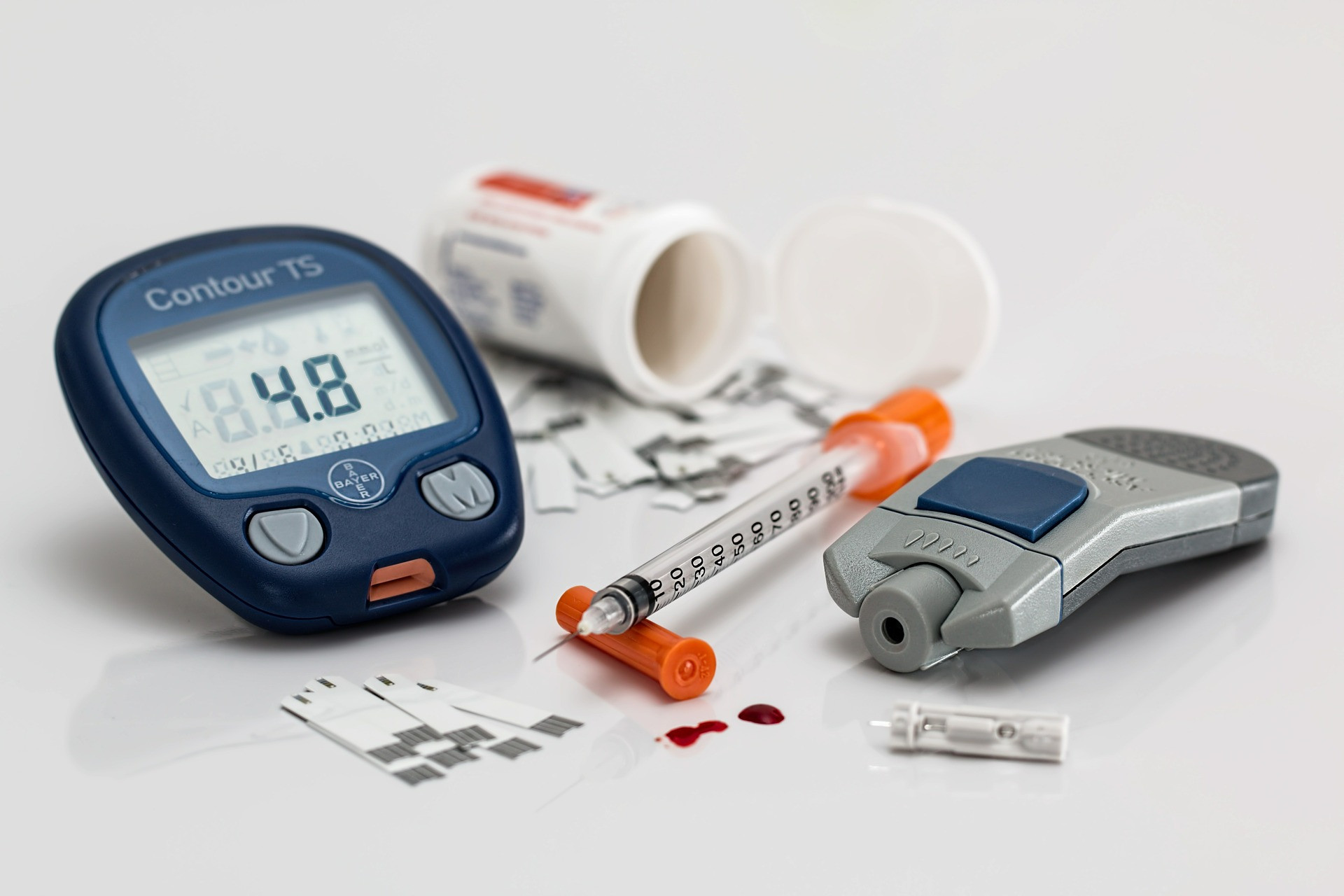
To debunk the misconceptions about A1c levels, we first need to understand what they are and how they function in our bodies. Let's unravel this concept in its simplest terms. A1c refers to glycated hemoglobin. It's a type of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body, that is bonded with glucose, or sugar.
In simpler terms, A1c levels provide a sneak peek into the blood sugar levels in the body over the past two to three months. Now, one might wonder, how are these A1c levels measured? The process is quite straightforward. When you go for your routine check-up, a healthcare provider takes a blood sample. This sample is then analyzed in a laboratory.
The results are given in terms of a percentage. For example, an A1c level of 7% indicates that 7% of your red blood cells are glycated. The higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar levels have been over the past few months. Thus, by measuring A1c levels, healthcare professionals can gauge a patient's long-term blood sugar control.
A critical point to note is that A1c levels aren't influenced by daily fluctuations in blood sugar levels but reflect the average levels over an extended period.
This aspect is often misunderstood and leads to the misconception that a single high or low blood sugar reading can significantly alter A1c levels, which is not the case. Understanding A1c levels is fundamental to managing diabetes effectively.
Misconceptions, if left unchecked, can hinder this process. However, with accurate knowledge and understanding, individuals can take better control of their condition.
Misconception 1: A1c Levels are the Only Indicator of Diabetes Control
It's a common and significant misconception to view A1c levels as the singular, ultimate litmus test for diabetes management. This misunderstanding may stem from the prevalent use of this test, as it does offer valuable insights into blood glucose control over a two to three-month period. However, it doesn't paint the complete picture. The A1c test, by design, provides an average. It isn't able to differentiate between extreme highs and lows, making its interpretation somewhat tricky.
An individual may experience wild swings in glucose levels and still end up with an A1c that appears to be in the normal range. Consequently, relying solely on this test can give a false sense of security or control. The truth of the matter is that diabetes control is multi-faceted.
Imagine a day-to-day life scenario. How does your body react to various meals? What about the influence of physical activity or the lack thereof? Even stress and sickness can dramatically affect blood sugar levels.
Frequent daily blood glucose monitoring is, therefore, essential in understanding these fluctuations and making necessary adjustments. The importance of lifestyle habits cannot be overstated. Nutritious food choices, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management are the pillars of good diabetes management.
They offer a crucial balance that complements medical treatments and A1c level monitoring. It is a symphony of these various factors, working in harmony that leads to effective diabetes control. Remember, diabetes control isn't a one-note song, but a richly textured orchestra, where every instrument, or in this case, every factor, plays its part.
Misconception 2: A 'Normal' A1c Level Means No Diabetes
Another widespread misconception is the belief that a 'normal' A1c level signifies the absence of diabetes. This belief, unfortunately, oversimplifies a much more complex physiological condition. It might seem logical at first glance. After all, doesn't 'normal' mean 'healthy'? Not necessarily, especially when it comes to A1c levels and diabetes. Let us delve into this a bit further.
A1c levels can and do fluctuate, influenced by myriad individual health factors. These include age, race, pregnancy status, and certain medical conditions. For instance, conditions such as anemia can affect A1c test results, potentially leading to misleading conclusions about one's diabetes status. It's also worth noting that some individuals may have 'normal' A1c levels, yet still experience significant blood glucose variability throughout the day.
Furthermore, 'pre-diabetes' is a condition characterized by blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. A person with pre-diabetes can have an A1c in the 'normal' range yet be at significant risk for developing full-blown diabetes.
Therefore, while a 'normal' A1c level can be part of a healthy picture, it does not categorically exclude the presence or the risk of diabetes. Both monitoring A1c levels and understanding its role within the broader context of individual health factors and daily blood glucose variations are crucial in the successful management of diabetes.
Misconception 3: Lower A1c Levels are Always Better
It's a common belief that when it comes to A1c levels in diabetes control, lower is always better. However, this is a misconception that might lead to unnecessary risks. The A1c level reflects the average blood sugar level over a period of about 2-3 months. So, the logic of the lower the level, the better the diabetes control, may appear to make sense, but it doesn't always hold true.
The idea that pushing for the lowest possible A1c level is best can lead to the dangerous situation of hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels. Symptoms can range from mild, such as confusion and sweating, to severe, including loss of consciousness or even seizures.
Healthcare professionals typically aim to balance A1c levels to avoid both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia. This balance is crucial as it ensures a person with diabetes can lead a healthy life without the immediate dangers of hypoglycemia and the long-term complications of persistent hyperglycemia.
Misconception 4: A1c Levels Can Be Lowered Quickly
One might be led to think that with strict diet and rigorous exercise, A1c levels can be rapidly reduced. This is another misconception that needs to be addressed. The truth is that A1c levels represent an average of blood glucose levels over several weeks.
Thus, a sudden change in lifestyle habits is unlikely to have an immediate significant impact on A1c levels. Improving A1c levels is a long-term commitment. It involves implementing sustainable lifestyle changes, which include balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, and possibly medication.
These changes should not be extreme but rather moderate and maintainable over the long haul. Rapid, drastic changes might not only be unsustainable but could potentially lead to other health problems.
Misconception 5: A1c Test Results are Always Accurate
It's easy to believe that laboratory diabetes tests, such as the A1c test, always give accurate results. However, this isn't always the case. Several factors can influence the accuracy of A1c test results. These include certain medical conditions like anemia or kidney disease, and even pregnancy.
In such cases, the A1c test may not be reliable, and healthcare professionals may need to use other methods to assess blood glucose control. Other factors, such as certain genetic traits, can also affect the A1c reading, making it appear higher or lower than it truly is. Thus, it's crucial to view A1c test results as one piece of the diabetes control puzzle, to be considered alongside daily blood glucose readings and overall health status.
Misconception 6: A1c Levels are the Same for Everyone
It's a common misconception that A1c levels are the same across the board for everyone. However, A1c levels can vary significantly based on a variety of factors. These include age, with older adults typically having higher A1c levels. Race is another significant factor, with certain ethnic groups tending to have higher A1c levels.
Moreover, it's important to remember that each person with diabetes is unique. What works for one individual might not work for another. Therefore, individualized treatment plans, based on personal health status and lifestyle, are essential in managing diabetes effectively.
In conclusion, understanding these misconceptions can be immensely beneficial in successful diabetes control. The journey of managing diabetes is not a sprint but a marathon, requiring a nuanced understanding and a holistic approach.
Misconception 7: A1c Levels Can Determine Daily Blood Sugar Levels
It's a notion that's been floating around, misguiding many: the belief that Hemoglobin A1c levels can offer a precise snapshot of daily blood glucose levels. Unveiling the truth, however, reveals this to be a profound misconception, leading individuals astray in their journey to maintain balanced blood sugar levels. For starters, let's understand what A1c is.
Hemoglobin A1c, commonly referred to as A1c, is a type of hemoglobin with glucose attached. It's measured to get an overall view of average blood sugar levels over a period of about three months. Yet, in attempting to paint a picture of one's daily blood glucose levels, A1c may offer a somewhat blurred image. Why so, you may ask? Let's delve into this.
When we speak of daily blood sugar levels, we refer to the readings from glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring devices. These are real-time values and can fluctuate based on food intake, exercise, stress, illness, and medication, among other factors. In a nutshell, if you are checking your daily blood sugar levels, you are looking at a snapshot of your glucose levels at a specific moment.
In contrast, A1c is akin to a long-exposure photograph, condensing a three-month span into a single frame. The two are distinct and serve different purposes.
Misconception 8: A High A1c Level Means Immediate Complications
Treading on to another widespread misconception, some believe that a high A1c level is tantamount to a siren wailing, signaling immediate complications. The truth, however, is slightly more nuanced and requires a deeper understanding of how diabetes works. For clarity, a higher A1c level is indeed a cause for concern. It indicates that your blood sugar levels have been relatively high over the past few months.
And yes, prolonged periods of high blood sugar can lead to complications related to diabetes. Nonetheless, the keyword here is "prolonged." Complications from diabetes don't spring up overnight, even with a high A1c level.
They are usually the result of consistently high blood sugar levels over a significant period, often years. Let's think of it as a river eroding its banks. A single flood might not cause significant changes, but consistent high water levels will, over time, alter the landscape.
Similarly, the complications associated with diabetes—like heart disease, kidney damage, or nerve damage—develop gradually. For instance, nerve damage due to diabetic neuropathy doesn't happen instantly with a spike in A1c levels. It occurs over years of high blood sugar levels that damage the nerves.
Hence, while a high A1c level is certainly a red flag warranting attention and action, it doesn't mean complications are imminent. It's a wake-up call to reassess and readjust one's approach towards managing diabetes, emphasizing the importance of long-term control and management.
Misconception 9: A1c Levels Can Be Managed Without Lifestyle Changes
There's a commonly held misconception floating around, one that suggests that A1c levels can be managed without making any lifestyle changes. The truth, however, isn't that simple, and it's important to dispel such myths for a proper understanding of A1c management.
For a start, it's necessary to comprehend that A1c, an indicator of blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, isn't just influenced by medication alone. In reality, it's intimately connected to our lifestyle choices.
The belief that one can control A1c levels without adjusting daily habits is, unfortunately, mistaken. This is due to the fact that our daily habits, including what we eat and how active we are, greatly impact our body's insulin response and glucose metabolism, which directly affect A1c levels.
Diet, in particular, plays a significant role. A diet filled with refined sugars, for instance, can result in blood sugar spikes, leading to elevated A1c levels. On the contrary, a balanced diet, packed with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, can stabilize blood sugar levels, and consequently, A1c levels. It's like a tug of war. On one side, unhealthy foods push your A1c levels higher.
On the other, healthy foods work tirelessly to bring it back down. Other lifestyle factors such as stress management and adequate sleep also have a profound effect on A1c levels. Chronic stress and lack of sleep can increase the body's insulin resistance, thereby raising A1c levels. Thus, it becomes evident that a holistic approach is imperative for managing A1c levels.
Misconception 10: A1c Levels are Only Important for People with Diabetes
The next misconception we're debunking is the idea that A1c levels only matter for individuals with diabetes. While it's true that monitoring A1c is essential for diabetes management, its importance extends beyond just this group. A1c is a vital indicator for prediabetes—a condition where blood sugar levels are high, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Prediabetes can silently progress to type 2 diabetes if left unchecked, which underscores the necessity of keeping an eye on A1c levels. Yet, its significance doesn't stop at prediabetes.
A1c levels also reflect one's overall health, making it important for everyone, not just those at risk of diabetes. High A1c levels can indicate an increased risk of heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage, regardless of diabetes status.
It’s akin to a silent alarm system, alerting you to potential health issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. The importance of A1c levels transcends the boundary of diabetes and reflects a much broader perspective of our health. In essence, the measurement of A1c levels is a proactive step towards preventive healthcare, helping to catch potential issues early before they become more serious problems.
So, the misconceptions that A1c levels can be managed without lifestyle changes, and that they're only important for people with diabetes, are misleading.
A1c management necessitates active lifestyle changes, and its relevance stretches beyond diabetes to prediabetes and overall health. Unveiling these misconceptions can pave the way for better health outcomes and improved disease prevention.
The Truth About Managing A1c Levels
When it comes to the subject of diabetes, managing A1c levels is critical, yet often overlooked. This essential component of diabetes management serves as the lighthouse guiding us through the rough waters of this challenging condition. An A1c level represents a long-term measure of blood sugar control, and its effective management could spell the difference between a life lived in good health and one fraught with complications.
The fact is, managing A1c levels requires more than merely popping a pill every day. Indeed, it entails a comprehensive and holistic approach to ensure optimum control. Understandably, it's not an easy feat. It requires effort, dedication, and perseverance.
Yet, the rewards are monumental. To manage A1c levels effectively, the first tip is to integrate regular physical activity into your routine. Exercise can aid in reducing blood sugar levels, and subsequently, A1c.
However, one should consult their doctor before undertaking any vigorous exercise plan. Second, a balanced diet is pivotal. An eating plan that prioritizes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables while limiting sugary foods and beverages can work wonders.
Remember, it's not just about avoiding sugar; it's about overall nutrition. Lastly, never underestimate the power of routine blood sugar monitoring. These readings provide immediate feedback and can help you adjust your food intake or medication dose as needed.
The Role of Medical Professionals in Managing A1c Levels
Taking charge of your health doesn't mean going it alone. A crucial part of managing A1c levels lies in the professional guidance of healthcare providers. Medical professionals, armed with years of training and experience, can provide valuable advice and suggestions tailored to your specific condition and lifestyle. Healthcare providers aren't just there to treat you when you're ill.
They serve as allies on your health journey, helping you navigate the intricate path of managing A1c levels. Their role extends beyond prescribing medication. They educate, counsel, monitor progress, and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Essentially, they form the bedrock of your diabetes management team. In this regard, it's essential to communicate effectively with your healthcare provider about your A1c levels.
Open and regular communication can significantly enhance your understanding of your condition and lead to better outcomes. A simple tip to keep in mind is to prepare for your appointments. Write down any questions or concerns you may have, and don't hesitate to bring them up during your visit. Remember, there are no silly questions when it comes to your health.
The truth is, managing A1c levels is a complex process that requires a comprehensive approach and a supportive healthcare team. However, with dedication, effective communication, and the right strategies, it's certainly achievable. Remember, each small step you take brings you closer to better health and a higher quality of life.
About The Author
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of "The Ultimate Diabetes Book," and founder of "the SugarMD YouTube channel."
Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn’t intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
466 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products