
UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE






Prevent Neuropathic Ulcer Foot


Table of Contents
- Causes of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
- Blood Circulation Issues
- People with Diabetes
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Symptoms of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
- Lack of Sensation
- Open Sores
- Affected Area
- Prevention of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
- Managing Blood Sugar
- Taking Care of Blood Vessels
- Understanding Why Ulcers Occur
- Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- SugarMD Neuropathy Support
- Conclusion
- About The Author
Neuropathic ulcer foot is a complex condition that affects many individuals, particularly those with underlying health issues such as diabetes. These ulcers are open sores that develop on the foot, often in areas where pressure and friction are most common. Understanding neuropathic ulcer foot requires a deep dive into the anatomy of the foot the nervous system and the circulatory system.
The foot's intricate structure consists of bones, muscles, nerves and blood vessels, all working together to provide support, balance and mobility. When something goes awry in this complex system, such as nerve damage or poor blood circulation, neuropathic ulcers can develop. The term "neuropathic" refers to the nerves and in the context of neuropathic ulcers, it's the damage to the nerves in the foot that leads to the loss of sensation.
This lack of sensation means that pressure or injury to the foot may go unnoticed, leading to the development of an ulcer. But what causes this nerve damage and how does poor blood circulation play a role in the development of neuropathic ulcers?
Causes of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
The causes of neuropathic ulcer foot are multifaceted and often interconnected. They can be broadly categorized into issues related to blood circulation, diabetes, peripheral neuropathy and lifestyle factors. In this section, we will focus specifically on blood circulation issues.
Blood Circulation Issues
Blood circulation is the process by which blood is transported throughout the body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to various organs and tissues. When it comes to the foot, proper blood circulation is crucial for keeping the skin, muscles and nerves healthy and functioning optimally. Understanding blood circulation in the foot involves recognizing the rich network of blood vessels that supply blood to every part.
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood to the foot, while veins return oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart. Capillaries the smallest blood vessels, facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and tissues. When blood circulation is compromised the foot may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to the breakdown of skin and underlying tissues, making them more susceptible to injury and infection.
Over time, this can result in the formation of an ulcer. Several factors can contribute to poor blood circulation in the foot, including arterial diseases, blood clots, obesity, smoking and a sedentary lifestyle. Each of these factors can restrict blood flow, leading to conditions that favor the development of neuropathic ulcers. The connection between blood circulation and nerve health is also vital.
Nerves rely on a steady supply of blood to function properly. When blood circulation is impaired, nerves may become damaged or die, leading to a lack of sensation in the foot. This lack of sensation is a key factor in the development of neuropathic ulcers, as it allows injuries to go unnoticed. Preventing blood circulation issues involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes.
Regular check-ups, a healthy diet, exercise and avoiding smoking can go a long way in maintaining good blood circulation. Blood circulation plays an essential role in the health of the foot and is a key factor in the development of neuropathic ulcers.
Understanding how blood circulation works, recognizing the factors that can impair it and taking proactive measures to maintain good circulation are crucial steps in preventing neuropathic ulcer foot. The complexity of this issue highlights the importance of a holistic approach to foot health, considering not only the physical structure of the foot but also the intricate interplay between the circulatory and nervous systems.
People with Diabetes
Diabetes is intrinsically linked to the development of neuropathic ulcer foot. People with diabetes often struggle with high blood sugar levels which over time can damage both the blood vessels and nerves in the foot. This damage impairs blood circulation and leads to a loss of sensation, creating conditions conducive to the development of ulcers.
Furthermore, diabetes is associated with insulin resistance and chronic inflammation, conditions that can further contribute to the deterioration of blood vessels. Changes in the foot's shape due to diabetes can lead to foot deformities, creating pressure points more prone to injury and ulceration. Additionally, a lack of awareness and education about proper foot care among people with diabetes can lead to neglect, further increasing the risk of ulcers.
Preventing neuropathic ulcers in people with diabetes is a complex task that involves careful management of blood sugar levels, regular foot examinations, proper footwear and education about foot care. Early detection and intervention are crucial in preventing the progression of ulcers.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy the damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, is another significant cause of neuropathic ulcer foot. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, including sensory, motor and autonomic functions. Sensory neuropathy leads to a loss of sensation, meaning that minor injuries or pressure on the foot may go unnoticed.
Without prompt treatment these minor injuries can develop into ulcers. Motor neuropathy can lead to muscle weakness and foot deformities, further increasing the risk of ulcers. Autonomic neuropathy impacts involuntary functions like blood vessel dilation which can also contribute to ulcer development.
Several factors can cause peripheral neuropathy, including diabetes, alcohol abuse, infections and certain medications. Understanding and addressing these underlying causes is essential in preventing neuropathic ulcers. Treatment often involves addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms and taking preventive measures such as medication, physical therapy, lifestyle changes and proper foot care.
It's worth noting that diabetes is a common cause of peripheral neuropathy. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage peripheral nerves, creating a vicious cycle where both diabetes and peripheral neuropathy contribute to the development of neuropathic ulcers.
Symptoms of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
Among the various symptoms that characterize neuropathic ulcer foot the lack of sensation stands out as a particularly troubling and complex issue. This symptom is not only a key indicator of the condition but also a contributing factor to its development and progression.
Lack of Sensation
The sensation is a vital part of our interaction with the world. It allows us to feel pain, heat, cold, pressure and other stimuli. In the context of the foot, sensation plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, avoiding injury and recognizing when something is wrong. Understanding lack of sensation, also known as sensory loss or numbness, requires delving into the anatomy and function of sensory nerves.
These nerves transmit information from the skin and other tissues to the brain. When they are damaged or impaired the transmission of sensory information is disrupted, leading to a lack of sensation. This damage can occur due to various underlying conditions, such as diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, or poor blood circulation. The role of lack of sensation in neuropathic ulcer foot is multifaceted. It creates a dangerous situation where injuries, pressure points, or other problems may go unnoticed.
Without the normal warning signals of pain or discomfort, a small injury or irritation can escalate into a serious ulcer. For example, wearing tight shoes or stepping on a sharp object might not be felt, allowing the injury to worsen over time. Detecting a lack of sensation in the foot can be challenging, especially in the early stages. Regular foot examinations by healthcare professionals, as well as self-examinations, can help in early detection.
Tools like monofilament testing, where a thin filament is pressed against the skin to assess sensation, are commonly used. The impact of lack of sensation on daily life can be disconcerting and disruptive. It affects daily activities such as walking, exercising and even simple tasks like putting on shoes. The constant vigilance required to avoid injury can be mentally taxing, leading to anxiety and stress. Prevention and management of lack of sensation involve addressing the underlying causes, such as controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes or improving blood circulation.
Regular foot care, including proper footwear, foot hygiene and professional foot examinations, is essential to prevent complications. While this section focuses on the lack of sensation, it's important to recognize that this symptom is often interconnected with other symptoms of neuropathic ulcer foot. The lack of sensation can lead to other issues such as open sores, infections and deformities, creating a complex web of interrelated problems.
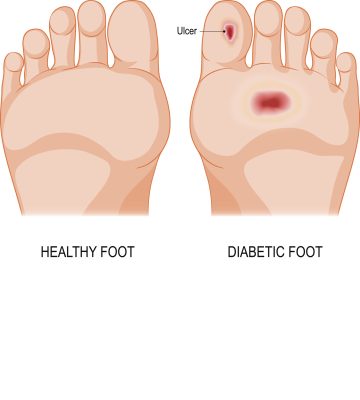
Open Sores
Open sores are a hallmark of neuropathic ulcers and often the first visible sign of this condition. These sores can vary in size and depth, appearing as wounds or breaks in the skin. They may be shallow or deep, with irregular or well-defined edges and the color of the wound may vary from red to dark brown. These sores typically occur in areas of the foot that are subject to pressure and friction, such as the ball of the foot the heel, or the big toe.
Surprisingly, pain may or may not be present with neuropathic ulcers. The lack of sensation due to nerve damage may mean that the person is unaware of the wound, allowing it to worsen without intervention. Infected ulcers may produce an unpleasant odor and may have discharge, signaling a more serious underlying infection. Open sores related to neuropathic ulcers often heal slowly or not at all due to the lack of blood flow to the area and the underlying nerve damage.
Affected Area
The affected area surrounding the open sore can provide additional information about the nature and severity of the neuropathic ulcer. Swelling and redness in the area around the ulcer may indicate inflammation, a natural response to injury that can exacerbate pressure on the wound and hinder healing. The affected area may feel warmer to the touch compared to the surrounding skin, a sign of infection or inflammation.
Chronic pressure or friction may lead to the presence of calluses or corns near the ulcer, contributing to its development. The skin around the ulcer may become dry, cracked, or discolored, indicative of underlying circulatory problems. A lack of sensation or altered sensation in the affected area is a key feature of neuropathic ulcers, leading to unnoticed injuries and the development of an ulcer.
Symptoms of neuropathic ulcer foot, particularly the appearance of open sores and the characteristics of the affected area, are vital in diagnosing and treating this condition. Understanding these symptoms, being vigilant in monitoring the feet and seeking medical intervention when these signs are present can prevent complications and promote healing. The complexity of neuropathic ulcers requires a comprehensive approach that considers not only the visible symptoms but also the underlying causes, including nerve damage and circulatory problems. Early detection and appropriate care are essential in managing neuropathic ulcer foot effectively.
Prevention of Neuropathic Ulcer Foot
Preventing neuropathic ulcer foot is a complex and vital task, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Among the various prevention strategies, managing blood sugar levels is a critical factor. This section will explore the importance of blood sugar management in preventing neuropathic ulcers.
Managing Blood Sugar
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for the body's cells. It's derived from the food we eat and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to both the blood vessels and nerves in the foot, impairing blood circulation and leading to a loss of sensation. This environment is conducive to the development of ulcers, making blood sugar management a vital preventive measure. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is the first step in effective management.
Understanding how different foods, activities and medications affect blood sugar levels is essential. Tools like continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices and regular blood tests can provide valuable insights. Diet plays a crucial role in blood sugar management. Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats and vegetables and avoiding processed and sugary foods, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity also helps the body use insulin more efficiently thereby controlling blood sugar levels. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial, but consultation with healthcare providers to determine the best exercise regimen is essential.
For some individuals, medication may be necessary to control blood sugar levels. Working closely with healthcare providers to understand the right type and dosage of medication is essential. Regular follow-ups and adjustments may be needed based on ongoing monitoring. Education about the importance of blood sugar management and its connection to foot health is vital. Support from healthcare providers, family and support groups can make the process more manageable.
Proper foot care is an integral part of blood sugar management in the context of preventing neuropathic ulcers. Regular foot examinations, proper hygiene and appropriate footwear can prevent minor injuries from developing into ulcers. Managing blood sugar levels is not without challenges. It requires a concerted effort, ongoing monitoring and a willingness to make lifestyle changes. Individualized care plans, considering unique health conditions and lifestyle factors, are often necessary.
Taking Care of Blood Vessels
The health of blood vessels is paramount in maintaining the well-being of the foot. Healthy blood vessels ensure that the foot receives an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients, essential for the skin, muscles and nerves to function properly. When blood vessels are compromised, it can lead to a lack of sensation and the development of ulcers.
Several factors can affect the health of blood vessels, including high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, smoking, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. These factors can lead to atherosclerosis, where the blood vessels become narrowed and hardened, restricting blood flow. Taking care of blood vessels involves a combination of medical interventions and lifestyle changes. Regular medical check-ups can help detect and manage underlying health conditions that may affect blood vessels.
Lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise and avoiding smoking can also contribute to maintaining healthy blood vessels. The connection between the health of blood vessels and the risk of developing neuropathic ulcers is direct.
Healthy blood vessels provide the necessary nourishment to the foot, preventing the conditions that can lead to ulcers. Conversely, impaired blood vessels can create an environment where ulcers are more likely to develop.
Understanding Why Ulcers Occur
Understanding why ulcers occur is a critical step in prevention. Ulcers occur when there is a breakdown in the skin, often due to constant pressure or friction. This breakdown can be exacerbated by underlying health conditions such as poor blood circulation and nerve damage. The lack of sensation means that the injury may go unnoticed, leading to the development of an ulcer.
Proper foot care plays a vital role in understanding why ulcers occur. Regular inspection of the feet, proper footwear and immediate attention to any injuries can prevent the conditions that lead to ulcer formation. Individual risk factors such as diabetes, peripheral neuropathy and lifestyle choices can contribute to the development of ulcers.
Understanding these risk factors and managing them effectively can prevent ulcers. Preventive measures include regular foot examinations by healthcare professionals, proper foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear and managing underlying health conditions. Education on foot care and understanding why ulcers occur can empower individuals to take proactive measures to prevent ulcers.
Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Diabetic foot ulcers are a prevalent and severe complication of diabetes, often leading to neuropathic ulcers. The treatment of these ulcers requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes, promotes healing and prevents recurrence. Among the various treatment options available, SugarMD Neuropathy Support has emerged as an innovative and effective solution.
SugarMD Neuropathy Support
SugarMD Neuropathy Support is a homeopathic supplement designed to protect nerves from damage caused by blood glucose and other oxidative assaults. Unlike prescription medicines for neuropathy, this supplement focuses on creating the right environment for nerves to breathe, thrive and naturally reestablish function. The ingredients in SugarMD Neuropathy Support include Benfotiamine which protects and maintains the health of the vascular wall that may be damaged by high blood sugar.
Alpha-lipoic acid boosts nerve anti-oxidant defense against neuropathy, while Acetyl L-Carnitine fights nerve damage, memory loss and cognitive decline. B12 protects the nerve myelin sheath, essential for preventing diseases like neuropathy. Vitamin B6 helps protect nerve endings and Vitamin D has neuroprotective effects, helping to prevent oxidative damage to the brain and nervous tissue.

SugarMD Neuropathy Support works by providing essential nutrients that support nerve health. The combination of vitamins and compounds in the supplement targets the underlying causes of neuropathy, helping to repair and regenerate damaged nerves. By enhancing blood flow and reducing inflammation, it promotes a healthy environment for nerve function.
Individuals with diabetic foot ulcers, peripheral neuropathy, or those at risk of developing these conditions can benefit from SugarMD Neuropathy Support. It's suitable for those looking for a non-prescription, natural approach to nerve health. SugarMD Neuropathy Support is typically taken as a daily supplement, following the instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare provider.
Consistent use, along with a healthy lifestyle, can lead to noticeable improvements in nerve function and overall foot health. As with any supplement, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using SugarMD Neuropathy Support, especially if you have existing health conditions or take other medications. The supplement is generally considered safe, but individual responses may vary.
Conclusion
The treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, particularly neuropathic ulcers, is a complex and multifaceted challenge. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes, a targeted approach to healing and ongoing care to prevent recurrence. SugarMD Neuropathy Support offers a promising solution in this context, providing a natural, homeopathic approach to nerve protection and regeneration.
The ingredients in SugarMD Neuropathy Support are carefully selected to address the specific needs of individuals with neuropathy, offering protection, repair and support for nerve function. By integrating this supplement into a broader treatment plan, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their foot health and overall well-being.
In the broader context of diabetic foot care, SugarMD Neuropathy Support represents a valuable tool in a holistic approach to prevention, treatment and ongoing management. It underscores the importance of recognizing the interconnected nature of our body's systems and the need for targeted, personalized care.
The journey to healing and preventing diabetic foot ulcers is a continuous process, requiring awareness, commitment and the right support. With products like SugarMD Neuropathy Support, individuals have access to innovative solutions that empower them to take control of their health, paving the way for a future free from the pain and complications of neuropathic ulcers.
About The Author
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic.
Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of "The Ultimate Diabetes Book," and founder of "the SugarMD YouTube channel."
Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn’t intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
466 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products









