UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE






Hypoglycemia: Causes, Symptoms and Solutions


Table of Contents
- What is Hypoglycemia?
- What Causes Hypoglycemia?
- Diabetes
- Medications
- Low-Carb Diets
- Alcohol Consumption
- What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
- Sweating or chills
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- What are the Conventional Medical Treatments for Hypoglycemia?
- Eat Regularly
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine
- Exercise Regularly
- What Novel Therapies Exist for Hypoglycemia?
- Artificial Pancreas
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
- Intrauterine Device (IUD)
- What Dietary and Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Hypoglycemia?
- Dietary Changes
- Lifestyle Changes
- What Natural Supplements Can Help Manage Hypoglycemia?
- Chromium
- Magnesium
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
- Berberine
- FAQs about Supplements and Hypoglycemia
- Can hypoglycemia be treated naturally?
- What vitamin deficiency causes hypoglycemia?
- What herb is good for hypoglycemia?
- Which vitamin helps stabilize sugar levels?
- How do you reverse hypoglycemia naturally?
- About The Author
Hypoglycemia is a condition in which the levels of glucose or sugar in the blood become too low. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and solutions of hypoglycemia, as well as three novel therapies, dietary and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition, and more.
What is Hypoglycemia?
Hypoglycemia is a condition characterized by low blood sugar levels. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels fall too low, the body's cells do not have enough energy to function properly. This can cause a wide range of symptoms, such as weakness, fatigue, confusion, irritability, sweating, and rapid heartbeat.
Hypoglycemia can be caused by a number of factors, including diabetes, certain medications, alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions. It is important to note that hypoglycemia can be serious, especially if left untreated, it is essential to monitor blood sugar levels and consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect you have hypoglycemia.
What Causes Hypoglycemia?
Diabetes
Diabetes is a common cause of hypoglycemia. When a person has diabetes, their body is unable to produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that regulates the levels of glucose in the blood. Insulin helps to move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is used for energy. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
People with diabetes who use insulin or certain oral diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas, are at a higher risk for hypoglycemia. This is because these medications can cause the pancreas to produce too much insulin, which can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low. In addition, people with type 1 diabetes, who rely on insulin injections, are more likely to experience hypoglycemia because they need to match the insulin dose with the amount of carbohydrates they consume.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia can occur suddenly, and they can be mild or severe. Mild symptoms include sweating, tremors, and heart palpitations. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures and loss of consciousness. It is important for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and to be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia. They should also work closely with their healthcare provider to adjust their treatment plan as needed to prevent hypoglycemia.
For people with diabetes, it is important to eat regular meals and snacks, to avoid skipping meals or going too long without eating, to be aware of the carbohydrate content of foods and to adjust insulin or oral diabetes medications accordingly, and to be physically active.
In addition, people with diabetes should always carry a source of sugar, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice, with them in case they experience symptoms of hypoglycemia. It is also important to have a plan in place for managing hypoglycemia and to be familiar with the signs and symptoms so that they can take action quickly if needed.
Medications
Medications can cause hypoglycemia by stimulating the pancreas to produce too much insulin, leading to low blood sugar levels. Medications that can cause hypoglycemia include:
- Insulin: Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When a person with diabetes uses too much insulin or takes it at the wrong time, it can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low.
- Sulfonylureas: Sulfonylureas are a class of oral diabetes medications that stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. When taken in high doses or in combination with other medications, they can cause hypoglycemia.
- Meglitinides: Meglitinides are another class of oral diabetes medications that work by stimulating the pancreas to produce insulin. Like sulfonylureas, they can cause hypoglycemia when taken in high doses or in combination with other medications.
Certain medications for other conditions: Some medications used to treat other conditions, such as birth control pills, corticosteroids, and some antidepressants, can affect insulin and glucose metabolism and may cause hypoglycemia.
It's important to note that not all people who take these medications will experience hypoglycemia and that the risk of hypoglycemia can vary depending on factors such as the type and dose of medication, as well as the individual's medical history and current health status. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional and report any symptoms of hypoglycemia when taking any medication.
Low-Carb Diets
Low-carb diets can cause hypoglycemia in diabetics because they restrict the amount of carbohydrates that are consumed. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose in the body, which is used for energy. When diabetics consume fewer carbohydrates, their blood sugar levels may drop too low because their bodies are not receiving enough glucose to function properly.
For people with diabetes, it's important to match their insulin dosage or oral diabetes medication with the amount of carbohydrates they consume. A low-carb diet may mean that a person with diabetes is taking more insulin or medication than they need, which can lead to hypoglycemia. Additionally, when following a low-carb diet, diabetics may struggle to consume enough calories, and this can lead to low blood sugar levels as well.
They may also experience hypoglycemia due to changes in their physical activity level, as the low carbohydrate intake may affect their energy levels. It's important for diabetics to work closely with their healthcare provider and dietitian to create a meal plan that is tailored to their specific needs.
Low-carb diets may not be appropriate for everyone, and it's crucial to make sure that the diet is balanced and provides enough energy to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. It is also important for people with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and to be aware of the symptoms of hypoglycemia. They should also work closely with their healthcare provider to adjust their treatment plan as needed to prevent hypoglycemia.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol consumption can cause hypoglycemia in diabetics because it interferes with the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. When alcohol is consumed, the liver prioritizes metabolizing the alcohol over glucose, which can lead to a decrease in blood sugar levels. Additionally, alcohol can also increase insulin secretion, which can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low.
This can be particularly dangerous for people with diabetes who are taking insulin or certain oral diabetes medications, as these medications can cause the pancreas to produce too much insulin, which can cause blood sugar levels to drop even further. It is important for people with diabetes to be aware of the effects of alcohol on blood sugar levels and to limit their alcohol consumption or avoid it altogether.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms so that you can treat it before it become serious. Here are common symptoms of hypoglycemia. Shaking or trembling When your blood sugar level drops, you may feel shaky or trembling, especially in the legs or arms. This symptom is a sign that your body is having difficulty regulating its blood sugar level.
Sweating or chills
You may experience perspiration or chills when your body is trying to maintain its blood sugar level. If you feel too hot, or if you feel cold, you may be experiencing hypoglycemia.
Nausea
When your blood sugar levels drop, you may feel nauseous or dizzy. This can also be a sign of hypoglycemia.
Fatigue
Feeling tired or fatigued is a common symptom of hypoglycemia. This is because your body is not getting enough glucose, the main source of fuel for cells.
Confusion
Low blood sugar levels can lead to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and trouble with short-term memory. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to check your blood sugar levels and seek medical attention if needed. If you experience any of these symptoms of hypoglycemia, it is important to seek medical attention right away.
The sooner your blood sugar levels are restored to a normal range, the quicker you can feel better. Treatment for hypoglycemia may include taking glucose tablets, eating specific foods that contain glucose, or taking insulin injections. With proper care and management, hypoglycemia can be managed successfully.
What are the Conventional Medical Treatments for Hypoglycemia?
Eat Regularly
When it comes to managing hypoglycemia, a key strategy is to eat regularly and consistently. Eating regularly throughout the day helps to keep blood sugar levels stable, avoiding blood sugar crashes and the associated symptoms of hypoglycemia. To maintain stable blood sugar, try eating three meals and two snacks a day. Your meals and snacks should consist of healthy carbohydrates such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, dairy and other protein-rich foods.
Healthy carbohydrates provide the body with energy, fiber, and vitamins and minerals. These foods also raise blood sugar slowly and over a longer period of time, compared with foods that are high in sugars and refined grains. It’s helpful to think about the timing of your meals. If you have meals at consistent times during the day, this will help your body know when to expect food and when to break down and absorb nutrients from those meals. This can help you to avoid hypoglycemic episodes.
Eating regularly throughout the day can also help you to better manage stress levels since stress can also contribute to hypoglycemia. If you’re feeling especially lightheaded, dizzy, or low in energy, try eating a high-carbohydrate snack. This can help to raise your blood sugar quickly. Examples of good snacks include nuts and raisins, apple slices with almond butter, or yogurt with fruit.
These snacks are a good source of healthy carbohydrates that will raise your blood sugar and help you to avoid hypoglycemic episodes. Eating regularly throughout the day is an essential part of managing hypoglycemia. Try incorporating healthy carbohydrates into your meals and snacks, and eating at consistent times throughout the day. This will help to keep your blood sugar stable and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia.
Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
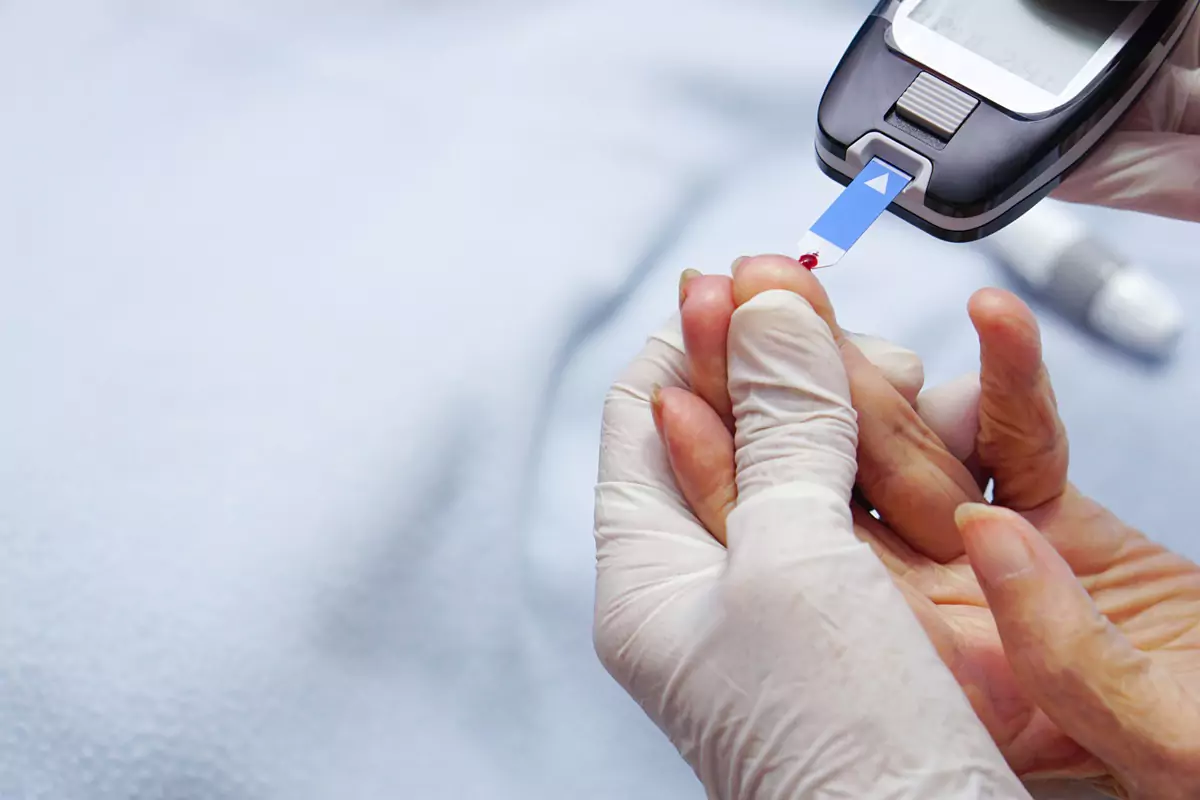
Monitoring one’s blood sugar levels is an essential step in managing hypoglycemia. Keeping track of glucose levels can help to detect patterns that may be causing episodes of hypoglycemia and can inform treatment decisions. Blood sugar levels can be monitored with a finger stick glucose test, which measures the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood taken from the fingertip.
This test, which can be done in the comfort of one's own home, can be done multiple times per day to keep track of the fluctuations in glucose levels. If a person’s blood sugar levels are consistently low, they may need to use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). A CGM is a device that monitors glucose levels in the body 24 hours a day, seven days a week. Rather than taking a sample of blood, a CGM instead uses a tiny sensor inserted under the skin that constantly measures glucose levels and sends the data to the wearer.
It is important to note that checking glucose levels isn't a one-off event. It is important to continually monitor glucose levels throughout the day to have a full picture of how the body is responding to dietary and lifestyle changes. Keeping track of glucose levels can help to avoid episodes of hypoglycemia and inform future treatment decisions.
It is recommended that adults with diabetes check their glucose levels as often as recommended by their healthcare provider, which is usually three to four times a day. When checking blood sugar levels, it is important to keep in mind the desired target range, which should be discussed with one's healthcare provider. A target range of 70-130 mg/dL (3.9 to 7.2 mmol/l) is generally recommended.
It is important to always have an extra glucose source on hand in case of low blood sugar levels. Fruits, candies, or energy gels are good sources of glucose and can help to bring glucose levels back to normal if needed. By closely monitoring one’s glucose levels and having an extra source of glucose on hand, one can take control of their hypoglycemia and manage it effectively.
Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine
Avoiding alcohol and caffeine is an important step in managing hypoglycemia or low blood sugar. Both alcohol and caffeine can cause blood sugar to drop and worsen symptoms of hypoglycemia. Excessive alcohol consumption can have a direct effect on hypoglycemia. Consuming too much alcohol can cause a drop in blood sugar, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, headache, confusion and sweating.
In addition, alcohol can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar in the long term, which can result in frequent and severe hypoglycemia. In extreme cases, it can even lead to alcohol poisoning, a life-threatening condition. Caffeine can also cause hypoglycemic episodes. Caffeine acts as a stimulant, so drinking any caffeinated beverage can lead to a surge of adrenaline and an increase in blood sugar.
Over time, this results in the body becoming “dependent” on caffeine and the need to continue consuming it in order to feel the same energy and alertness. Unfortunately, this heightened state of alertness can ultimately lead to a crash in blood sugar, resulting in hypoglycemic symptoms. For those who suffer from hypoglycemia, abstaining from alcohol and caffeine is essential.
Cutting out these substances can help control and manage hypoglycemia. Avoiding caffeine and alcohol may be difficult for some, and it’s important to note that everyone’s response to these substances may be different. If you are experiencing any symptoms of hypoglycemia, seek medical advice from a healthcare professional.
Exercise Regularly
Exercising regularly is key to managing hypoglycemia and reducing its symptoms. Regular physical activity can help regulate your blood sugar levels, increase your insulin sensitivity, and reduce the amount of insulin you need to take. For people with hypoglycemia, exercise is one of the most important lifestyle changes you can make. Exercise helps to reduce your risk of developing diabetes, improves blood sugar control, and reduces body fat and weight, all of which are important factors in managing blood sugar.
Some of the best types of exercise for managing hypoglycemia are aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, and biking. These types of activities improve your body’s ability to use sugar for energy. Strength training is also beneficial for musculoskeletal health and for regulating sugar. Be sure to monitor your blood sugar levels before and after exercising, and stop immediately if you experience dizziness or other signs of hypoglycemia.
Additionally, consume some carbohydrates before beginning exercise, and have a snack or meal afterward. This will help ensure that your blood sugar stays in a safe range. It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the best exercise plan for you. Depending on your specific needs, they may recommend an individualized program that includes moderate to vigorous exercise, strength training, and activities that you enjoy doing.
Exercising regularly is an important part of managing hypoglycemia, and can help you live a healthier, more active lifestyle. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you, and remember to monitor your blood sugar levels during physical activity.
What Novel Therapies Exist for Hypoglycemia?
In recent years, novel therapies for hypoglycemia have been developed. These therapies can help people with hypoglycemia to manage their condition and reduce the risk of dangerous symptoms and complications. In this section, we will look at three of the most promising novel therapies available.
Artificial Pancreas
One of the most attractive novel therapies for hypoglycemia is the use of the artificial pancreas. An artificial pancreas is a device that monitors glucose levels and then administers insulin when needed. This device can be programmed to allow for individualized glucose control, thus eliminating the need for frequent monitoring and multiple insulin injections. There are currently several clinical trials for the use of the artificial pancreas in people with hypoglycemia and the results are showing great promise.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
Another novel therapy for hypoglycemia is the use of continuous glucose monitors (CGM). CGMs are small devices that can be placed under the skin which constantly monitor glucose levels. They can provide real-time information about glucose levels and can alert the user if their glucose is too low or too high. This therapy can help people to better manage their hypoglycemia and prevent dangerous episodes.
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Finally, the use of an intrauterine device (IUD) may be a novel therapy for hypoglycemia. An IUD is a small device that is inserted into the uterus and can release hormones to regulate the body's blood sugar levels. Studies have shown that the use of an IUD can reduce the risk of serious episodes due to hypoglycemia.
All three of these therapies offer promising solutions for people with hypoglycemia. Each person should discuss these therapies with their doctor to determine if they are a good option for their condition. With the help of these novel therapies, people with hypoglycemia can find relief from their symptoms and reduce the risk of dangerous episodes.
What Dietary and Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Hypoglycemia?
When dealing with hypoglycemia, making adjustments to one's diet and lifestyle can help manage and reduce symptoms. Below are some dietary and lifestyle changes individuals can make to help manage their hypoglycemia:
Dietary Changes
Eating small, frequent meals
Eating smaller and more frequent meals throughout the day can help keep blood sugar levels balanced and reduce hypoglycemia. It is also important to eat complex carbohydrates such as whole grain breads and vegetables as opposed to simple carbohydrates such as cookies and cakes that can cause blood sugar swings.
Limiting high levels of sugar
Limiting high levels of sugar can help hypoglycemia by preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. High levels of sugar can cause the pancreas to release too much insulin, which can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low. By limiting high levels of sugar in the diet, it can help to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent hypoglycemia. It also helps in reducing the risk of developing diabetes, obesity and other related health conditions.
Incorporating more complex carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates break down more slowly in the body than simple carbohydrates, providing a steady source of energy. This can help to prevent blood sugar levels from dropping too low, which can help to prevent hypoglycemia.
Eating complex carbs such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes and nuts may help regulate blood sugar levels by providing a steady source of energy. These foods are also a good source of other important nutrients such as fiber, vitamins and minerals. It is important to monitor carbohydrate intake, and adjust insulin or oral diabetes medications accordingly, as well as to work with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized diet plan.
Lifestyle Changes
Stress Management
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels and can contribute to the development of hypoglycemia. Stress causes the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar levels. However, stress can also lead to changes in eating habits, such as skipping meals or overtaking medications, which can also affect blood sugar levels in opposite.
Managing stress through techniques such as relaxation, mindfulness, and deep breathing can help to reduce the impact of stress on blood sugar levels and can help to prevent hypoglycemia. Additionally, incorporating regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and eating a healthy diet can also help to manage stress and improve overall health.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy and other forms of psychotherapy can also be effective in managing stress and preventing hypoglycemia. These therapies can help individuals to identify and address the underlying causes of stress and to develop coping strategies to manage stress in a healthy way.
It's important to note that stress management is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it's essential to try different techniques to find what works best for you, and to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses any underlying medical conditions and addresses any potential side effects of the treatment.
Monitoring Medications
Monitoring medication can help in hypoglycemia by ensuring that any medications that are being taken are not causing or contributing to low blood sugar levels. Some medications, such as insulin and certain oral diabetes medications can cause hypoglycemia as a side effect. Additionally, some medications, such as beta-blockers, can mask the symptoms of hypoglycemia, making it difficult to recognize and treat.
By monitoring the medications, an individual can identify any potential side effects and work with their healthcare professional to adjust the treatment plan as needed. This can include adjusting the dosage, switching to a different medication, or taking the medication at a different time of day. It's also important to be aware of any potential interactions between medications, as some medications can increase the risk of hypoglycemia when taken in combination with certain other medications.
It's important to note that it's not always clear that medication is causing hypoglycemia, so monitoring blood sugar levels, symptoms, and any other possible causes is crucial. If an individual suspects their medication is causing hypoglycemia, they should consult with their healthcare professional, who can help to determine the cause and suggest appropriate treatment. Making adjustments to one’s diet and lifestyle is a key part of managing and reducing symptoms of hypoglycemia.
By eating smaller, frequent meals, limiting foods high in sugar and simple carbohydrates, exercising regularly, managing stress levels and drinking plenty of water, individuals can help reduce the impact of hypoglycemia. It is also important to speak to a healthcare provider to find the best treatment for one’s specific situation.
What Natural Supplements Can Help Manage Hypoglycemia?
There are several natural supplements that may help manage hypoglycemia, some of them are given as below:
Chromium
Chromium is a mineral that plays an important role in insulin function and blood sugar regulation. Studies have shown that chromium supplements can improve glucose metabolism and lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Chromium also helps to increase insulin sensitivity, which can be beneficial for those with hypoglycemia caused by insulin resistance.
Magnesium
Magnesium is an essential mineral that is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body, including glucose metabolism. Magnesium deficiency is common in people with diabetes, and low levels of magnesium have been linked to insulin resistance and an increased risk of hypoglycemia. Magnesium supplements have been found to improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha-lipoic acid is a powerful antioxidant that has been found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. ALA is an antioxidant that is found in small amounts in certain foods, such as spinach, broccoli, and potatoes. It can also be taken as a supplement. Studies have shown that ALA can improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of developing diabetes. It may also help to prevent or improve nerve damage caused by diabetes.
Berberine
Berberine is a compound found in certain plants, such as Berberis vulgaris and Coptis chinensis. It has been traditionally used in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine to treat various health conditions, including diabetes. Studies have found that Berberine can improve glucose metabolism and lower blood sugar levels. This can be achieved by activating an enzyme called AMPK, which regulates glucose metabolism. Berberine also has been found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
It is important to note that before taking any supplement, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you are taking any medications or have any underlying medical conditions, as some supplements may interact with medications or have side effects. Also, it's important to be aware that supplements are not meant to replace a healthy diet and lifestyle, so it's important to maintain a healthy diet, regular exercise and monitor your blood sugar levels as directed by healthcare professionals.
Best Supplement on Berberine
SugarMD Super Berberine is a dietary supplement that supports healthy glucose metabolism and reduces inflammation. Its unique formula combines dihydroberberine and 100% pure Ceylon cinnamon to effectively maintain healthy blood sugar levels while also reducing inflammation. Not only is Super Berberine 5 times more absorbable than regular berberine, but it also aids in weight loss by activating AMPk levels and supporting fatty acid intake.
In addition to its benefits for glucose metabolism and weight loss, Super Berberine also serves as a powerful antioxidant and anti-aging agent through the activation of AMPk levels. Unlike other supplements, Super Berberine exclusively uses pure Ceylon cinnamon, which is of higher grade and completely safe for regular use. Unlike Cassia cinnamon, which contains coumarin, pure Ceylon cinnamon does not pose a risk of toxicity.
FAQs about Supplements and Hypoglycemia
Can hypoglycemia be treated naturally?
Yes, hypoglycemia can be treated naturally through dietary changes. Eating frequent, small meals throughout the day can help regulate blood sugar levels. This can be done by incorporating more complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables, as well as protein and fiber, into meals and snacks.
Complex carbohydrates break down more slowly in the body, providing a steady source of energy, while protein and fiber can help slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Additionally, reducing the intake of refined sugars and processed foods, and incorporating physical activity into daily routine can also help improve blood sugar control.
What vitamin deficiency causes hypoglycemia?
A deficiency in vitamin B1 (thiamine) can cause hypoglycemia. Vitamin B1 plays an important role in metabolism, and deficiency in this vitamin can lead to an inability to convert glucose into energy, resulting in low blood sugar levels. Symptoms of thiamine deficiency include fatigue, muscle weakness, and irritability. Thiamine can be found in foods like whole grains, nuts, and seeds, as well as in supplements.
What herb is good for hypoglycemia?
Gymnema Sylvestre, a herb traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine, may help lower blood sugar levels and improve symptoms of hypoglycemia. Gymnema Sylvestre has been found to stimulate the pancreas to produce insulin and to inhibit the absorption of sugar in the intestines.
It may also improve glucose tolerance and reduce cravings for sugar. Gymnema sylvestre can be taken in supplement form, but it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Which vitamin helps stabilize sugar levels?
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Vitamin B1 is important for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the production of energy. Without enough vitamin B1, the body cannot convert glucose into energy, leading to low blood sugar levels. Vitamin B1 can be found in foods like whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes, as well as in supplements.
How do you reverse hypoglycemia naturally?
To reverse hypoglycemia naturally, it is important to make dietary changes such as increasing complex carbohydrates, fiber, and protein in the diet, and to eat more frequent small meals throughout the day. Additionally, incorporating physical activity into daily routine, and avoiding refined sugars and processed foods can also help.
Monitoring blood sugar levels and consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended. It is also important to address underlying causes of hypoglycemia, such as diabetes, liver or kidney disease, or an overactive thyroid, and to take any medication as prescribed.
About The Author
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin's journey in the medical field began with earning his medical degree with honors from Marmara University School of Medicine in Istanbul, Turkey. He then went on to complete his internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic, one of the top medical centers in the United States, located in Cleveland, Ohio.
With a wealth of knowledge and experience in his field, Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, making him a respected and highly qualified physician. He is also a certified diabetes education specialist, author of the book "The Ultimate Diabetes Book" and the founder of the SugarMD YouTube channel, where he shares valuable insights and information on diabetes management and care.
Currently, Dr. Ergin practices in Port Saint Lucie, FL, where he provides exceptional care to his patients and helps them to effectively manage their diabetes. It is important to note that the information on diseases and treatments provided on this website is for general guidance only and should never be considered a substitute for the advice provided by a qualified healthcare professional. Always seek the advice of your physician, health provider, or other qualified healthcare professional with any questions you may have regarding your health.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
466 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products