UP TO 40% OFF SITEWIDE






The Insulin Resistance Diet! Reverse IR Today!


Table of Contents
- How does insulin resistance develop, and what causes it?
- If you're wondering what insulin resistance looks like, here are some signs:
- Dietary strategies for reducing insulin resistance:
- Glycemic index: what is it? Low-glycemic-index eating diet plan:
- Fruits: Which fruits are best to consume if you have insulin resistance? Do they truly assist?
- Pomegranates
- Grapes:
- Strawberry:
- Guava:
- Cherries:
- Papaya:
- Oranges:
- Vegetables For Insulin Resistance Diet:
- Lean proteins:
- Legumes and Beans:
- Fish in Insulin Resistance:
- Treatment for Insulin Resistance With Medication or Homeopathic Remedies:
- Insulin Resistance Test;
- How to check insulin resistance
- These tests may involve the following:
- Are There Any Other Treatments Than Insulin That Can Help With Diabetes and Insulin Resistance?
- Ways to Reverse Insulin Resistance:
- How About Getting Rid of That Extra Weight?
- Conclusion:
- About the author:
- REFERENCES:
Understanding insulin resistance: Choose a diet to overcome it: Want to learn about the insulin resistance diet? You are in the right place. A large percentage of the American population is affected by Insulin resistance, and its presence often goes unnoticed and unchecked for a long time. Insulin resistance can lead to prediabetes and, if untreated, type 2 diabetes in adults.
Contrary to common perception, insulin resistance can be reversed with a sound insulin resistance diet and does not always lead to prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. It may serve as a valuable early warning indicator, prompting you to evaluate your food and lifestyle to see where changes can be made. Reversing insulin resistance, restoring energy, controlling sugar cravings, and decreasing the risk of many lifestyle-related diseases are all attainable with slight modifications to one's way of life.
How does insulin resistance develop, and what causes it?
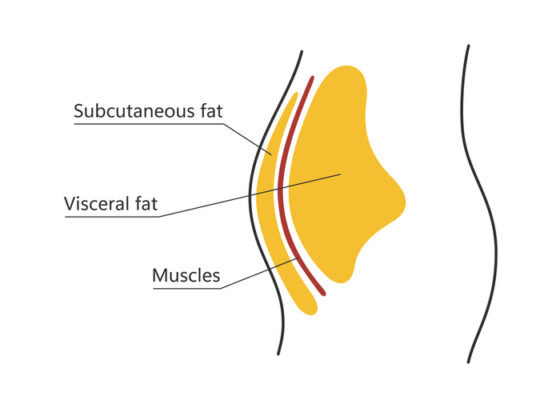
Visceral and subcutaneous fat around waistline. Location of visceral fat in abdominal cavity. Types of human obesity. Medical scheme. Vector illustration isolated on a white background. Can be fixed with insulin resistance diet
Glucose is the body's primary energy source, but it needs the hormone insulin to transport it from the bloodstream to the cells where it may be used. When you have insulin resistance, your cells refuse to respond to insulin, so the sugar in your bloodstream does not enter your cells. After that, your body tries to correct itself by making more insulin to stabilize your blood sugar levels.
Insulin is a hormone that regulates how glucose is taken up by cells, thereby influencing blood sugar levels. Insulin is a potent hormone made by your pancreas that facilitates glucose uptake by your cells. When a person has type 1 diabetes, the pancreas totally stops producing insulin because beta cells have been damaged. Those with type 1 diabetes cannot use glucose from food without insulin injections.
Insulin is produced by the pancreas of people having type 2 diabetes, but the body does not correctly respond to it. Thus some people with diabetes require insulin injections to help their bodies utilize glucose for energy. There are several types of insulin
- Regular or short-acting insulin
- Rapid-acting insulin
- Intermediate-acting insulin
- Long-acting insulin
If you're wondering what insulin resistance looks like, here are some signs:
If you have insulin resistance, you won't know it.
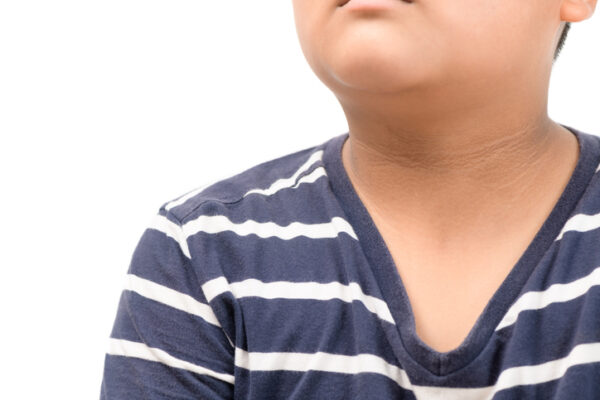

Black marks of the skin around the neck of overweight children isolated on white background, One of the warning signs of diabetes.
However, a disorder called acanthosis nigricans can manifest itself. This occurs when the skin in your armpit or neck grows darker. You may also develop skin tags in the same regions. Symptoms like these may present themselves if insulin resistance causes blood sugar levels to rise.
- An increased desire for urination
- Early fatigue and tiredness
- Increased thirst
- Tingling sensation on the bottoms of your feet
- Vision problems are also possible.
The person will show no symptoms if the pancreas can produce adequate insulin despite the resistance. But if their insulin resistance worsens with time, people can experience increased blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia. It's essential to be aware of typical symptoms of high blood sugar levels as it can help you take the suitable measures and receive the support and diagnosis you need.
Dietary strategies for reducing insulin resistance:
As for the good news? Eating the right foods can help lower insulin resistance and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Researchers are still trying to determine the exact relationship between diet and insulin resistance.
The key to improving insulin sensitivity and reducing insulin resistance is eating a diet rich in unprocessed, whole foods. White bread, cakes, cookies, and ice cream are all examples of highly processed meals that are high in simple sugars and can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels and, eventually, insulin resistance.
It has also been proven that eating foods like sausage, bacon, cheese, and butter, all heavy in saturated fats, might exacerbate insulin resistance.
Glycemic index: what is it? Low-glycemic-index eating diet plan:
Choosing carbs with low GI, Carbohydrates are crucial to our diets, but not all carbohydrates are supposed to be equal. The Glycemic Index (GI) measures the rate at which a carbohydrate-containing diet is converted into sugar and delivered into circulation.
Carbohydrates with a low Glycemic index value of 55 are digested, absorbed, and metabolized more slowly in the body, resulting in a slower rise in blood glucose and insulin levels. Low GI meals have been demonstrated to be advantageous for weight management and lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes.
In addition, they assist patients in regulating their blood glucose levels and decreasing insulin resistance. A perfect diet with a low glycemic index (GI) can also minimize the risk of insulin resistance in obese children. Your body digests meals with a low glycemic index more slowly. This indicates that your blood glucose levels gradually increase over time instead of skyrocketing. To learn more about the glycemic index click here.
Fruits: Which fruits are best to consume if you have insulin resistance? Do they truly assist?

Healthy fresh fruits in a wooden crate isolated on white background. The composition includes mango, banana, apple, fig, orange, kiwi, blueberry, lime, grape, strawberry, pear, peach, papaya, and watermelon among others. High-resolution 42Mp studio digital capture taken with Sony A7rII and Sony FE 90mm f2.8 macro G OSS lens. Good for insulin Resistance diet
The fiber content of whole fruits is another way in which they aid in blood sugar regulation and weight maintenance. Even if you have diabetes, you should still consume fruits. To maintain your body free of toxins and take advantage of their significant function in detoxifying, it is essential to eat a wide variety. There is no need for exotic fruits; eating fresh, local, and in season is most suited for you.
Pomegranates
Pomegranates are on the list of diabetic-friendly fruits. Pomegranates have the highest concentrations of antioxidants compared to other fruits, making them ideal for warding off free radicals and delaying the onset of chronic illnesses. You may safely indulge in these crimson gems containing potent phytochemical components.
Grapes:
Resveratrol, a phytochemical found in grapes, influences insulin secretion and action, influencing the body's blood glucose response. Since this is the case, grapes are a healthy option but not more than 10 grapes at a time to prevent blood sugar spikes.
Strawberry:
Strawberries have a low glycemic index, so the glucose they contain is absorbed slowly into the bloodstream. It can also enhance immunity, has the cancer-fighting capacity, and improves metabolism, which in turn helps you lose weight.
Guava:
A low glycemic index fruit that makes an excellent snack for diabetes. Constipation is a typical complaint among people with diabetes, but guava's high fiber content can help relieve this problem and reduce the risk of developing type-2 diabetes.
Cherries:
Cherries, like blueberries, are rich in anthocyanins, which increase insulin synthesis in cells by as much as 50 percent. There is hope that anthocyanins will one day form the basis of innovative therapies for diabetes. Thus, cherries should be incorporated into a balanced diet.
Papaya:
The fruit's natural antioxidants make it an excellent option for people with diabetes. High or low blood sugar levels can create various health problems for people with diabetes. A papaya-rich diet may enhance health and longevity by preventing further cell damage.
Oranges:
Flavonols, flavanones, and phenolic acid have been demonstrated to have significant preventive effects, particularly in those with diabetes. Citrus fruits reduce glucose updating and prevent glucose from being absorbed by the intestines and used by the liver.
Vegetables For Insulin Resistance Diet:

Fresh vegetable market stand. Good for insulin Resistance diet
Vegetables are the best source of vitamins and minerals and tend to be low in carbs and rich in dietary fiber. Nutrients are needed by the body to carry out its tasks. Glucose metabolism is a part of this. Plant chemicals called polyphenols in vegetables have antioxidant properties. Muscle and fat tissue glucose uptake can be hindered by oxidative stress, leading to decreased insulin secretion.
Antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can be found in varying amounts in vegetables of various colors. For that reason, it's wise to eat a wide variety of foods for your health. Spinach and kale are just two examples of leafy greens full of healthy nutrients. A, B, C, and K vitamins.
Peppers, tomatoes, and other red veggies Polyphenols, including anthocyanin, found in radishes and cabbage, may help reduce insulin resistance. Carotenoids are necessary for the body to produce vitamin A, and eating foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, and squash can help increase your body's supply.
Many white vegetables, including mushrooms, garlic, and onions, include antioxidants that help keep diabetes in check. In addition to helping to avoid diabetic problems, the antioxidants found in many vegetables play a role in doing so as well.
Evidence suggests that consuming dairy products may lower the chances of developing type 2 diabetes. Several dairy components, including calcium, vitamin D, dairy fat, and especially trans-palmitoleic acid, have been proposed as possible underlying mechanisms for this association due to their potential roles in obesity and metabolic syndrome.
It has been hypothesized that trans-palmitoleic acid, a fatty acid in dairy products like milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter, can significantly lower the risk of insulin resistance and conditions related to insulin resistance, like prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
Organic dairy products are preferable to conventional ones made from cow's milk when following a diet for insulin resistance. Raw cheese, yogurt, and sheep or goat milk are always superior choices. Brown rice, pasta, and bread are all examples of whole grains.
These foods are high in fiber and may lower the amount of sugar absorbed by the body after a meal containing both sweet and savory components. Portion control is significant when dieting or trying to reduce carbohydrate intake.
A full plate comprises high-fiber veggies, protein, and healthy unsaturated fats for low-carbohydrate diets.Here are some examples: Gluten-free, whole-grain flour (eg, wheat, buckwheat, millet), Oatmeal, Brown rice, and Barley.
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Excellent food sources include olive oil, vegetable oils, olives, avocados, seeds, almonds, and oily salmon.
Lean proteins:
White meat (poultry and fish) may predominate in this case, while darker meats (red and processed) take up a smaller percentage of the diet. In such a case, ensure you eat enough beans, lentils, and other pulses, as well as soy and tempeh, which are also high in protein.
Legumes and Beans:

Piles of a variety of healthy organic legumes. Good for insulin Resistance diet
The dietary fiber and polyphenols found in beans and legumes benefit health. Beans with rice are an excellent example of improvements in insulin sensitivity and A1C levels have been observed after consuming legumes (such as peas, chickpeas, black beans, and lentils). You can get a lot of healthy fats, as well as nutrients like magnesium, fiber, and protein, from nuts, seeds, and butter, without eating too many carbohydrates.
Eating low-carbohydrate meals has positive effects on blood sugar and insulin resistance since they do not cause as dramatic of a rise in blood sugar levels. Nuts are also a great source of healthy fats and protein, but eating the right amount of them is essential because they pack a lot of calories. If you can, go for raw and unsalted options.
Fish in Insulin Resistance:
Type 2 diabetes is so much more than just a blood sugar problem, which is the common perception. The characteristic of type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Heart disease and stroke are two times more common in those with type 2 diabetes compared to those people who do not have the condition.
Because of its high omega-3 fatty acid content, a salmon is a beautiful option of fish for those with type 2 diabetes, since this "good" fat can help lower the risk of common diabetes-related problems such as heart disease, heart failure, and stroke. Examples of high-omega-3-content fish are: Salmon, mackerel, herring, sardines, and tuna.
Treatment for Insulin Resistance With Medication or Homeopathic Remedies:
There is currently no FDA-approved medicine that is explicitly designed to reverse or treat insulin resistance. However, certain diabetic medications, such as thiazolidinediones and metformin, may help enhance your insulin sensitivity and reduce its effects on your body.
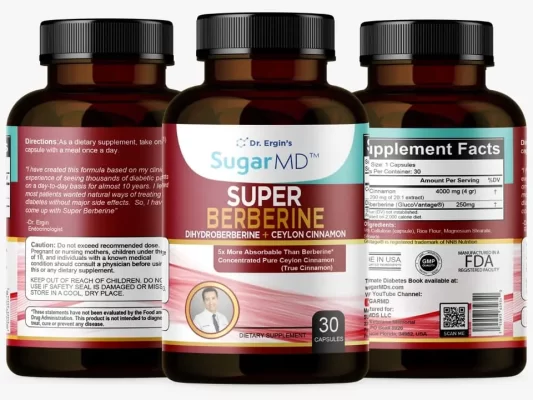
However, for those looking to go natural try Super Berberine which has Dihdyroberberine which is a 5 times more absorbable form of berberine along with concentrated Ceylon cinnamon both of which are proven effective for insulin-resistant and prediabetic patients. Insulin resistance can be treated, in conjunction with a balanced food plan, by contacting a healthcare practitioner for information on treatment options.
They may suggest that you speak with a dietician to receive individualized guidance.
Insulin Resistance Test;
How to check insulin resistance
In most cases, a healthcare expert will not test that is only focused on insulin resistance. On the other hand, insulin resistance can be shown by testing for prediabetes and diabetes. Yet if your doctor tests your fasting insulin and glucose levels they can calculate your HOMA score which can give a good idea of insulin resistance even before prediabetes is diagnosed when a1c is over 5.7%.
Computing an insulin resistance score may sound like complex math, but it's really a lot simpler than you think. All it amounts to is taking your fasting plasma glucose and fasting serum insulin values, then dividing them by 22.5 to get your HOMA-IR. The higher the number, the lower your body's sensitivity to insulin, otherwise known as 'insulin resistance'.
These tests may involve the following:
After you have been without food for at least 8 hours, a medical expert will perform a test called the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test. During this test, the professional will determine your fasting blood glucose levels.
The A1C test:
With the A1C test, your healthcare professional will collect measurements of your blood glucose for two to three months, and then they will use the average of those readings to determine if you have diabetes.
Oral glucose tolerance test:
During this test, you will consume a uniquely sugary beverage, and a medical practitioner will check your blood glucose levels after and before you finish the beverage. Approximately 2 hours are allotted for the test.
Are There Any Other Treatments Than Insulin That Can Help With Diabetes and Insulin Resistance?
Consuming a diet that is both nutritious and well-balanced may be beneficial for both weight loss and the maintenance of a balanced body weight. In addition, if you have insulin resistance, you want to make an effort to keep your waist circumference at or below 40 inches for males and 35 inches for females. Reversing insulin resistance can also be helped by maintaining a regular exercise routine.
Ways to Reverse Insulin Resistance:
Modifications to your lifestyle, even minor ones, can have a major effect on your ability to control insulin resistance.
Maintain an Active Lifestyle:
Your body will be better able to maintain a healthy balance of blood glucose levels if you engage in regular physical activity. When it comes to overcoming insulin resistance, high-intensity training is by far the most effective method.
Lose Some of That Extra Weight
One of the primary contributors to insulin resistance is the presence of excess fat throughout the body, particularly in the region of the waist. In addition to this, visceral fat secretes hormones into the bloodstream that cause inflammation, which can lead to insulin resistance. As a result, make it a priority to engage in a consistent exercise routine and consume a nutritionally sound insulin resistance diet.
Give attention to the right timings
Improving insulin resistance will be facilitated by increasing the amount of nutrient-dense foods consumed during the first half of the day. The next step is to prepare a balanced meal consisting of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats to keep the body fully working and energetic throughout the day.
Maintain a well-balanced diet
According to the findings of recent studies, eating an insulin-resistant diet that is high in nutrients and includes fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, foods that are high in fiber, dairy products, and healthy fats will have a beneficial effect on insulin resistance.
How About Getting Rid of That Extra Weight?
The National Diabetes Prevention Program and other lifestyle treatments result in weight reduction and may increase glucose tolerance. Because extra body weight and belly fat are connected to insulin resistance, even a decrease as minor as 10 pounds or 5% of your total weight can benefit.
Although very restricted diets could show visible effects right away, the weight reduction they cause is not always sustainable. It is possible that if you want to improve your insulin resistance and overall health, it will be more advantageous for you to focus on developing healthy behaviors rather than on losing weight.
Conclusion:
The most important thing to do on an insulin-resistant diet is to stick to the basic rules of good eating. If you follow an insulin-resistant diet, you won't have to worry about avoiding great things or starving yourself because it won't restrict your caloric intake. Instead, make sure that the majority of your diet consists of plant-based meals that are high in fiber.
Additionally, simple carbs should be avoided in the morning and early afternoon because these are the times of the day when an insulin rise is most likely to occur. It is essential to get regular exercise and make sure you are taking your medicine as directed, in addition to maintaining a healthy diet.
Even something as simple as going for a walk after eating or taking the stairs rather than the elevator can make a significant improvement. Insulin is a very strong hormone that is produced by your pancreas. Insulin is what permits your cells to absorb glucose, which is a sugar that your body utilizes as a source of energy in the food that you eat.
However, if you have insulin resistance, your cells will not be able to use the insulin that your pancreas produces as efficiently as they should. This condition is associated with type 2 diabetes. Alternatively, your pancreas could not produce any insulin at all, which is the situation with people who have type 1 diabetes.
Understanding what insulin resistance is and what foods to consume to control it is essential to both sustaining and having a healthy lifestyle, as forty percent of the population deals with some degree of insulin resistance.
If you have insulin resistance yourself, or if you have a loved one or a coworker who struggles with it, we suggest you share this article with them so that they may better understand it and learn the best sorts of foods to consume and the types of foods to avoid if they have insulin resistance.
About the author:

Fix insulin resistance with diet and supplements
Who is Dr. Ergin? Dr. Ahmet Ergin is an endocrinologist interested in and passionate about diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors at Marmara University School of Medicine in Istanbul, Turkey.
Then, he completed his internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio. He is a board-certified Internal Medicine and Endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism physician. He is also a certified diabetes education specialist.
Disclaimer: Any information on diseases and treatments on this website is for general guidance only and must never be a substitute for the advice your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional provides. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare professional with questions you may have regarding your medical condition.
REFERENCES:
Draznin, B., Aroda, V.R., Bakris, G., Benson, G., Brown, F.M., Freeman, R., Green, J., Huang, E., Isaacs, D., Kahan, S. and Leon, J., 2022. Summary of revisions: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes care, 45(Suppl 1), pp.S4-S7.
Association American Diabetes, 2018. Updates to the Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care, 41(9), pp.2045-2047.
Wilcox, G., 2005. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clinical biochemist reviews, 26(2), p.19.
Covington, M., 2004. Omega-3 fatty acids. American family physician, 70(1), pp.133-140.
Written By Dr. Ahmet Ergin
465 total articles
Meet Dr. Ahmet Ergin, a highly skilled and dedicated endocrinologist with a passion for diabetes care. Dr. Ergin earned his medical degree with honors from Marmara University in Istanbul. He completed internal medicine residency and endocrinology fellowship at Cleveland Clinic. Dr. Ergin is board-certified in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism due to his vast medical expertise. He's a certified diabetes educator, author of “The Ultimate Diabetes Book,” and founder of “the SugarMD YouTube channel.” Dr. Ergin offers exceptional diabetes care to his patients in Port Saint Lucie, FL, helping them manage effectively. For a closer look into his insights and experiences, connect with Dr. Ahmet Ergin on LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube.”
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Information on this website isn't intended to treat, cure or prevent any disease. Discuss with your doctor and do not self-treat.
Products